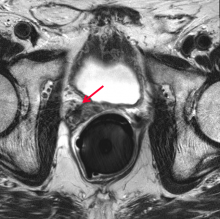
Over the last several years in the U.S., healthcare providers have been trying to shift their focus to more preventive care to keep healthcare costs down. This has placed a greater emphasis on screening large segments of the population for various diseases in an attempt to catch them earlier. Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) screening has emerged as a powerful tool in the early detection of lung cancer, following a B rating by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) in 2013.
If you enjoy this content, please share it with a colleague
- Read more about Upping the Numbers on Lung Cancer Screening
- Log in or register to post comments