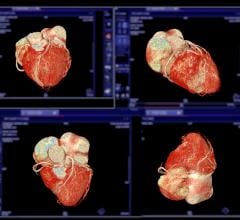
CTA is one of the most complex procedures routinely performed on a CT scanner. A successful CTA exam requires synchronization of the timing of the scan with maximum vessel contrast enhancement.
Several factors influence vessel enhancement. Some are patient-related, such as weight and cardiac output, while others are related to contrast, such as concentration and injection rate. It is well established that maximum vessel enhancement benefits from optimal contrast volume, injection rate, and contrast concentration. Modifying injection protocols for various patient populations can be quite challenging.
Further challenges in CTA
The latest generation of CT scanners offers wide coverage and fast rotation speeds, requiring updated contrast injection protocols to take full advantage of scanner features. CTA scans are also challenging from a post-processing perspective because they require significant 3D analysis for visualization and measurement of the vessel and its lumen.
With its patient focus and clinical integration, Philips Ingenuity CT provides the necessary tools and dedicated workflow to perform a successful CTA exam time after time. Following are some of the features:
SyncRight — The Philips SyncRight option provides seamless integration between the injector and scanner, facilitating the workflow of a CTA exam. Benefits of this include the ability to edit and view scanner and injection parameters and results using the scanner console. SyncRight simplifies operations and enhances overall consistency by streamlining workflow and reducing decision points by up to 50 percent. With SyncRight, the user can:
• Automatically load the injection protocol from the exam card to the injector
• Modify the injection protocol through scanner/injector console
• View injection timings and planned scan timings on scanner console
• Start injection and timed scans from scanner/injector console
• Produce the injection report as part of the exam summary series
Bolus tracking — BolusPro software on Philips Ingenuity CT allows the user to synchronize the start of the scan with predefined vessel enhancement. The user can place a region of interest on a vessel and define a Hounsfield unit threshold. Reaching a predefined threshold for vessel enhancement triggers the start of CT scanning.
Other tools on the Ingenuity CT allow users to manage the radiation dose involved in a CTA exam without compromising clinical details. Ingenuity CT also allows enhanced visualization of iodine versus calcium in the vessels.
Dose modulation — The Ingenuity CT scanner has several dose modulation features that reduce the radiation dose delivered to the patient:
• Automatic current setting for each patient based on patient size
• Longitudinal modulation of the tube current according to patient attenuation at every table position (ZDOM)
• Combined longitudinal and angular modulation of tube current (3DDOM)
In-room controls — The user can position the patient and start/stop the scan after setting up the IV contrast in the scan room.
The in-room countdown to X-ray “ON” updates the user on the amount of time left to leave the room before the X-ray starts.
Automatic MPR creation — Results driven scanning on Ingenuity creates automatic MPRs as predefined by the exam card. The user can save the needed MPRs for a particular exam as a part of the exam card for automatic generation after the scan is completed.
Scannable range — The scanner has a scannable range of 2000 mm, allowing the user to scan lower extremities of patients with peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
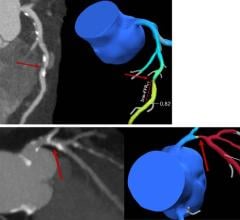
Advanced Vessel Analysis — The Advanced Vessel Analysis (AVA) package on the Extended Brilliance Workspace (EBW), Brilliance Workspace Portal, and IntelliSpace Portal provides automatic bone removal, vessel extraction with centerline creation, and labeling. This automatic processing noticeably simplifies workflow with rapid creation of results. The package also allows measurement and quantification of stenosis and aneurysm within a vessel, and also provides stent planning, generating a report with all measurements to send to the referring physician.
Dose reporting — A summary of the radiation dose delivered to the patient is saved with the patient’s exam and sent to PACS for future reference.
Contrast reporting — A summary of the patient injection parameters is saved with the patient’s exam and sent to PACS for future reference on the contrast dose delivered to the patient.
This case study was supplied by Philips Healthcare.



 May 17, 2024
May 17, 2024