Computed Tomography (CT) continues to be a rapidly evolving technology with many new advancements, as displayed and discussed at the Radiological Society of North America109th Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting (RSNA23).
As a whole, the computed tomography market size in the US in 2024 is estimated to be $2.38 billion, and expected to reach $3.18 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 5.86% in the forecast period (2024-2029), according to a new report released by Mordor Intelligence. The industry is seeing several notable trends in computed tomography, among them, coronary CT angiography (CCTA).
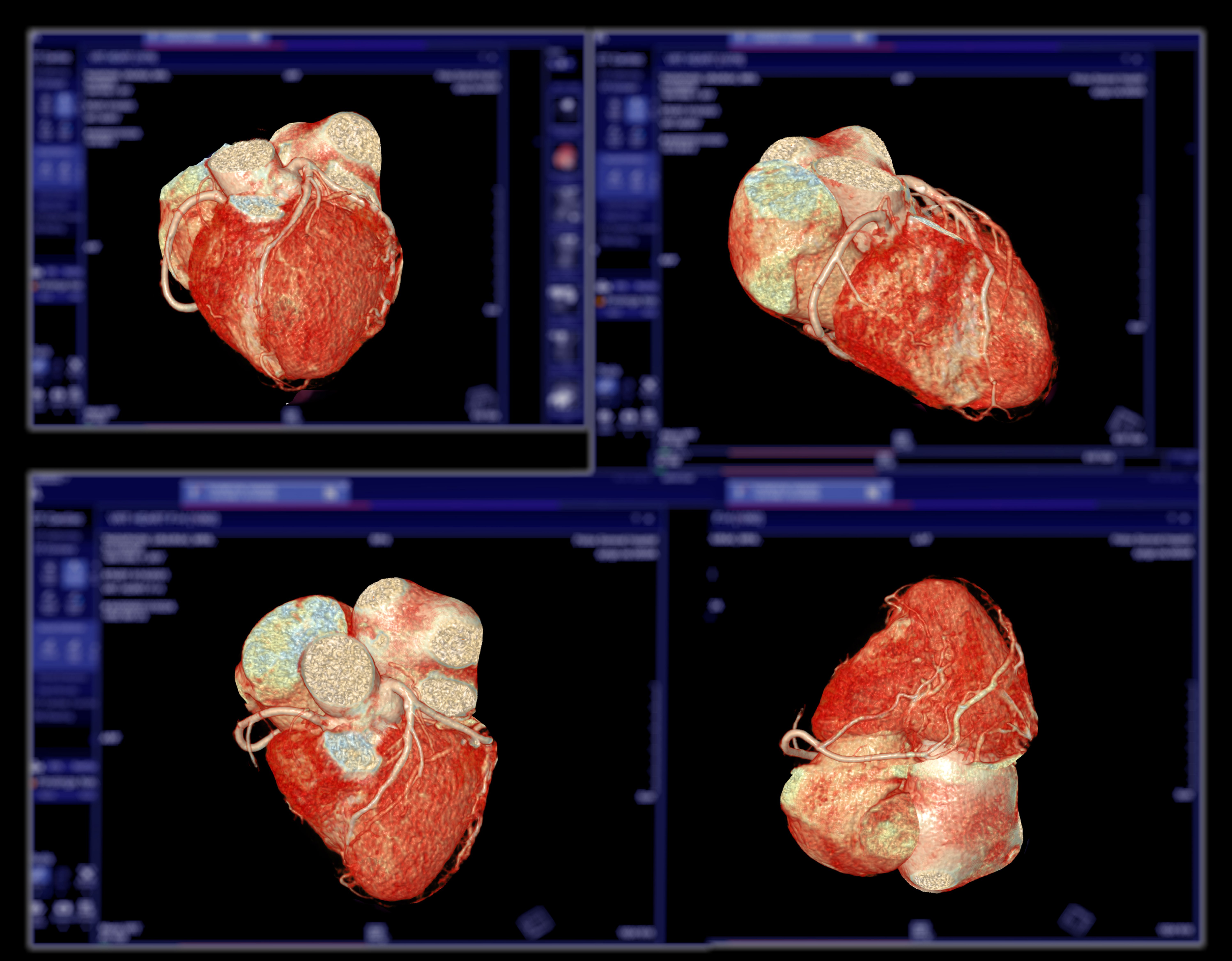
Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography Developments
At RSNA23, ITN had the opportunity to speak with Bhvita Jani, principal analyst at Signify Research, about advancements and trends in medical imaging, including the development of coronary CTA.
Jani shared that one of the biggest trends she is seeing this year within the advanced medical imaging space is development of coronary computed tomography angiography. “A lot of the CT product launches have been centered around this application,” she said. “The CT procedural mix is evolving, and cardiac CT is starting to account for a large proportion of that. I think especially with the recent changes in guidelines and the recommendation to use CT for screening of coronary artery disease, we expect to see this trend really impact the way CT is used in the future.”
To give some background, last year a joint expert consensus document was created based on input from the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography (SCCT), American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM), American College of Radiology (ACR), North American Society for Cardiovascular Imaging (NASCI) and Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) with endorsement by the Asian Society of Cardiovascular Imaging (ASCI), the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACI) and the European Society of Cardiovascular Radiology (ESCR). According to an abstract issued by the Journal of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography (JCCT), cardiac CT continues to expand with increasing applications and evolving technology.
The terminology used in the field was previously unified by consensus agreement of cardiologists, medical physicists and radiologists in 2006. To give the terminology a fresh look, a representative writing group with key stakeholders was reconvened to provide an update to the nomenclature of terms commonly used in clinical and research applications of cardiac CT. The purpose of the document was to consolidate multiple terms and provide clear definitions for terms applicable to cardiac CT. The document underwent organizational review by the SCCT Board of Directors and the AAPM board, as well as the ACR, NASCI and RSNA’s boards, in addition to peer reviewers.
“This is an update to the prior dated document with modernized terminology for evolving technology, including new photon counting computed tomographic machines,” said writing group co-chair and corresponding author Lynne Koweek, MD, FACR, FSCCT, in a previously released written statement. “Standardized terminology allows for consistency in communication across all members of the imaging community and will assist with clinical care and multicenter trials.”
A 2021 study published in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging focused on cardiac imaging trends over a decade. It reported the rate of CCTA exams by radiologists in hospital outpatient departments increased markedly from 2010 to 2019. Over that period, the rates of CCTA by radiologists in hospital outpatient departments increased by 355%, according to findings of Russell A. Reeves, MD, Ethan J. Halpern, MD, and Vijay M. Rao, MD, FACR, from Thomas Jefferson University Hospitals. Data was pulled from 2010–2019 Physician/Supplier Procedure Summary (PSPS) files obtained from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) website. According to Reeves, the increasing rate of CCTAs performed by radiologists represents a growing opportunity for collaboration in cardiac imaging.
CCTA’s Presence at RSNA23
As Jani observed, CCTA had a large and noticeable presence on the RSNA23 exhibit hall floor. Siemens Healthineers announced the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance of the Somatom Pro.Pulse, a dual-source CT scanner designed to be more affordable for a wide range of healthcare facilities. According to the company, the scanner combines the power and speed of dual-source CT technology with embedded artificial intelligence and user assistance features to deliver workflow efficiencies. Dual-source CT allows for high temporal resolution, which, along with scan speed, is important for cardiac CT scans to limit artifacts caused by breathing or cardiac motion.
In addition, Arineta Cardiac Imaging announced FDA 510(k) clearance of its SpotLight and SpotLight Duo family of cardiovascular CT scanners at RSNA23. According to the company, the Duo system adds high resolution thoracic clinical capability, suitable for screening lung cancer, COVID-19 and other pulmonary diseases. Both the SpotLight and SpotLight Duo systems add extended coverage for peripheral vascular and runoff studies, a rapidly growing procedure for vascular therapies. The SpotLight system is a 25 cm Field of View (FOV) dedicated CCT system, enabled by Arineta’s proprietary Stereo CT technology. SpotLight has best-in-class specifications for temporal resolution (120 msec), one beat whole-heart coverage (14 cm), spatial resolution (0.5 mm detector), and X-ray tube power for superior image quality (139 kW effective).
“The recent change in guidelines from the ACC and AHA are now clear that cardiac CT is the Level 1A evidence recommended test for diagnosis of stable and acute chest pain,” said Chaim Lotan, MD, professor at Hadassah-Hebrew University, in a written statement from Arineta. “According to the World Health Organization, four of the top six causes of death are cardiovascular and thoracic diseases.”
Other Notable CT Trends
Of course, the current application of CT technology runs deeper than just CCTA. Here is a brief overview of several significant developments in computed tomography.
Technology advancements. CT scanners continue to undergo technological advancements. Innovations such as dual-energy CT, wide-area detectors and iterative reconstruction techniques are contributing to enhanced image quality, faster scan times and reduced radiation doses.
AI integration. Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being integrated into CT workflows. AI algorithms are being utilized for image reconstruction, noise reduction and automated analysis, just to name a few. This integration aims to improve the accuracy and efficiency of radiological interpretations.
As an example, the US Department of Veterans Affairs has selected Riverain’s ClearRead CT AI-powered technology as part of its Lung Precision Oncology Program. Automated precision measurements with ClearRead CT leads to improved repeatability and consistency of imaging interpretation across different radiology readers, times of day and workload — increasingly important in this era of radiology burnout and talent shortage, according Steve Worrell, Riverain CEO, in speaking with ITN at RSNA23. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death for US veterans. Worrell emphasized that the use of this technology by the VA is an important step toward addressing health disparities in this population.
Thirona, a global company specializing in advanced analysis of thoracic CT images with AI, recently received FDA clearance for the latest update of its AI-based clinical software LungQ (v3.0.0), a solution that is capable of using AI to automatically segment the pulmonary segments and subsegments found in the internal anatomy of the lung.
The company says that based on this analysis, which includes the identification of structures such as lobes, segments, subsegments, airways and fissures, the technology performs an analysis of the lung tissue and the fissure completeness, supporting physicians in the diagnosis and documentation of pulmonary tissue images from CT thoracic datasets for each individual patient.
Clinical applications. CT imaging is finding expanded applications in various medical fields, such as the aforementioned cardiac CT, functional CT for perfusion imaging and 4D imaging. Radiologists are increasingly leveraging these advancements for more detailed and accurate diagnoses.
Dose reduction initiatives. There is a growing emphasis on minimizing radiation exposure in CT scans. To this end, low-dose CT imaging techniques and dose modulation technologies are being used to ensure patient safety while maintaining diagnostic quality.
Portable and point-of-care CT. Efforts are being made to make CT imaging more accessible in a variety of healthcare settings. Portable and point-of-care CT scanners allow for imaging in emergency situations, ambulances and critical care environments.
Workflow improvements. It is clearly a high priority and continued industry focus to develop new ways of improving workflow efficiency. Automated protocols, dose management systems and streamlined image reconstruction processes can be implemented to enhance the overall radiology workflow.
Collaboration with other specialties. Radiologists are increasingly collaborating with other medical specialties to provide comprehensive diagnostic information. This interdisciplinary approach is consistently contributing to more effective patient care.
Education and training. Ongoing education and training programs continue to be essential for radiologists to stay updated on the latest technologies and methodologies in CT. The benefits of continuing education prove to be invaluable.
Find more RSNA23 conference coverage here
Download ITN's Computed Tomography Systems comparison chart here


 December 05, 2025
December 05, 2025 









