December 16, 2022 — One in eight women develop breast cancer in their lifetime. 1 Regular screening mammograms can help save lives 2 as well as help women determine if they have dense breasts - an independent risk factor that is not as well-known but can double one’s risk for breast cancer. 3
Forty percent of women have dense breast tissue4 - which means they have a higher proportion of fibro glandular tissue than fatty tissue. While mammography is considered the most reliable imaging technique for breasts, limitations can exist due to breast density. 5 This is especially the case in dense breasts where tissues may overlap - hiding signs of breast cancer and making diagnosis more difficult or even missed. 6
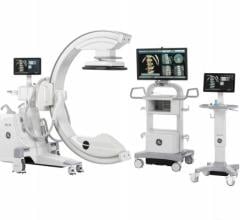
To provide a personalized breast screening approach for a diverse population, including those with dense breasts, GE Healthcare offers a comprehensive portfolio of breast imaging technologies, including the Senographe Pristina, a mammography system designed to provide a better patient experience, 8 and Invenia ABUS, the first FDA-approved ultrasound supplemental screening specifically designed for detecting cancer in dense breast.
When a result remains inconclusive after screening, GE Healthcare’s SenoBright HD Contrast Enhanced Mammography (CEM) can provide immediate follow-up when in search for a definitive answer. CEM combines mammography and vascular-based screening methods to highlight areas of unusual blood-flow patterns that may indicate malignancy - helping reduce the masking effect of fibro glandular breast tissue so lesions can be more clearly identifiable.7 8 9 A SenoBright exam can be performed in the same room as a mammogram, with the same equipment, and can even be performed the same day in about seven minutes10 as part of GE Healthcare’s aim to provide precision, comfort and efficiency across the entire clinical breast health continuum. If medical indications recommend pathology, biopsy under contrast with Serena Bright can also be performed from first image to last image within fifteen minutes. 11
In an effort to help further advance breast cancer and support healthcare providers in a starting a new contrast program, GE Healthcare’s new Pristina Bright** offering provides a comprehensive solution. Pristina Bright combines SenoBright HD, Pristina Serena, and Serena Bright with an education program that includes dedicated on-site support, CME accredited self assessment, as well as access to the users’ club where providers will be able to share with experts around the globe and leverage resources needed to market their facility among referring doctors and patients.
In addition to this offering and in continued pursuit to improve breast cancer outcomes, GE Healthcare has joined the Contrast-Enhanced Mammography Imaging Screening Trial (CMIST)12 in collaboration with the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (BCRF)to gain an increased understanding of the effectiveness of CEM in the detection of breast cancer in dense breasts. Early studies of CEM for women with dense breasts have shown the potential benefit of CEM in the detection of breast cancer. The CMIST study seeks to determine if contrast-enhanced mammography provides more accurate cancer detection compared to digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), including whether it reduces false-positive exams, in women with dense breasts.
The clinical power of contrast-enhanced mammography as well as our full suite of breast cancer care technologies will be featured in the debut of the One-Stop Clinic Experience for Breast at #RSNA22 (North Hall Room 8349). From days to hours, GE Healthcare’s One-Stop Clinic Experience will enable practitioners and healthcare providers to step into the shoes of patients for a truly immersive breast care experience that puts the spotlight on value-based care, rapid diagnosis to treatment planning, personalized and precise care, all while improving workflow, operational, financial outcomes.
As part of the One-Stop Clinic Experience for Breast, GE Healthcare will be showcasing its full suite of technologies across the patient care continuum, including:
Senographe Pristina : Regular screening increases the chances of detecting breast cancer early, when treatment is likely to work best.13 The Senographe Pristina mammography system was designed to ease anxiety the moment the patient enters the exam room. It features an inviting gantry with elegant lighting and rounded shapes, as well as a soft-curved surface that welcomes patients into a space of comfort and support. 83% of patients rated their experience with Senographe Pristina better and more comfortable than previous exams. 14 Today, Pristina continues to evolve and expand along the breast care pathway - including the option to use Pristina Dueta , an industry-first, patient- assisted compression remote control device that gives patients a sense of control around their breast compression during a mammogram while under the supervision of a technologist to minimize their discomfort.15
Invenia ABUS: Invenia ABUS 2.0 is a non-invasive and patient-friendly technology and helps to move Breast Care from reactive to proactive. When used as supplement to mammography, Invenia ABUS increases cancer detection in dense breasts by 35.7% and the additional mammography occult cancers found with ABUS were predominantly invasive and node negative16. Detecting cancer at this early stage has important prognostic implications and can reduce the total cost of care17. When breast cancers are found at Stage 1 and 2, 70% of patients may avoid chemotherapy18 . The new and powerful AI Assistant on Invenia ABUS 2.0 seamlessly integrates intelligent algorithms powered by FDA-approved third-party AI tools QVCAD and KOIOS DS Breast to assist in detecting and characterizing breast lesions, helping radiologists increase their reading speed and streamline their workflow with a great degree of confidence. The implementation of QVCAD experience up to 93% sensitivity for lesion detection19 and is leading into reducing reading time by 33%20. Koios DS Breast automatically provides an AI-based quantitative risk assessment that aligns to a BI-RADS® category with demonstrating a decrease of the benign biopsies by up to 31%.21 To support more precise treatment planning, the multiplanar ABUS views offer surgeons a complete view of the breast in 3D with a reproducible location of pathological findings. ABUS is a great tool for treatment planning and staging due to the coronal plane access, as the full extension of the breast cancer is demonstrated in a standardized view to provide an accurate assessment of the peritumor stromal involvement and potential multiplicity of the cancer.
LOGIQ E10 Series: Detecting and characterizing breast disease, especially in women with dense tissue, can be challenging. Radiologists and sonographers need the highest quality imaging combined with productivity tools to provide definitive answers as efficiently as possible. The LOGIQ E10 Series helps clinicians make a real difference in the lives of patients with breast disease. The systems’ cSound Architecture provides images of excellent detail and contrast resolution for greater diagnostic confidence, while new AI-based workflow tools help increase exam efficiency, including: Breast Productivity Package, Breast Assistant,22 and Auto Lesion Segmentation.
SenoBright HD Contrast Enhanced Mammography (CEM): Performed as a follow-up to an inconclusive mammography and ultrasound, SenoBright HD highlights areas of unusual blood flow patterns, so practitioners can precisely see what matters. SenoBright HD provides advanced image quality with high specificity to help reduce false-positives and to help prevent unnecessary biopsies and surgeries.23 The exam can be performed in less than seven minutes24 – using the same mammography equipment, in the same room, with the same staff. Delivering clear image quality, CEM offers a high level of confidence for clinicians and patients.
Breast Biopsy Solutions: If medical indications recommend pathology, Pristina Serena 3D Biopsy transforms a Senographe Pristina screening room into an interventional suite in just two minutes with the dedicated add-on biopsy kit without requiring a long and mechanical needle installation. Clinicians now have the option of accessing the breast with the newly designed “side approach” to access a larger working space for ease of patient positioning,reducing needle visibility to help ease patient anxiety and allow best access to lesions close to the breast support. GE Healthcare also offers the industry’s first contrast-guided biopsy solution Serena Bright™ Contrast-Guided Biopsy designed to biopsy lesions that are otherwise not clearly identifiable. The technology, which received U.S. Food and Drug Administration 510(k) clearance in May 2020, allows patients to have their breast biopsy exams with contrast guidance using the same mammography equipment, in the same room, and with the same staff as the screening or diagnostic mammogram.
ProFound AI 3.0: ProFound AI from iCAD for Senographe Pristina runs on an AI based algorithm trained to detect malignant soft tissue densities and calcifications. The algorithm’s confidence that a detection or case is malignant is scored on a 0 to 100 percent scale. A higher score indicates a higher level of confidence in the malignancy of the detection or case. These Certainty of Finding and Case Scores serve as a guide to help interpreting radiologists determine if a suspicious finding or case needs further workup. Profound AI can reduce reading time by an average of 52.7%, increases sensitivity by an average of 8%, and increases specificity by an average of 6.9%. 25
Cerianna (fluoroestradiol F18) Injection: Understanding estrogen receptors (ER) discordance in recurrent or metastatic breast cancer (MBC) enables clinicians to better adapt the treatment strategy of patients. Biopsy may not always be feasible in metastatic disease where the breast cancer has spread to distant organs and multiple sites26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33. The only imaging agent that detects whole-body ER+ lesions in MBC is Cerianna, a first-of-its-kind radioactive diagnostic agent approved in May 2020, which is indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) imaging for the detection of ER+ lesions as an adjunct to biopsy in patients with recurrent or metastatic breast cancer 34.
Lunar iDXA with enCORE v18 software: Cancer patients are at risk for reduced bone density following treatment. As part of the follow-up after breast cancer treatment, DXA exams can be performed. Advanced clinical applications like DXAVision provide bone mineral density and body composition in one easy, unified workflow, resulting in a DXA scan that is up to 40% faster than a traditional Total Body scan.35 Combined with TBS integration, and streamlined reporting with easier style sheets and formulas, enCORE v18 helps deliver more efficient workflows and ease the burden on technologists while streamlining patient throughput.
For more information: www.innovation.gehealthcare.com
Find more RSNA22 coverage here
References:
**Pristina Bright is a commercial offering including SenoBright HD, Pristina Serena and Serena Bright
1 https://www.breastcancer.org/facts-statistics
2 Løberg M, Lousdal ML, Bretthauer M, Kalager M. Benefits and harms of mammography screening. Breast Cancer Res. 2015 May 1;17(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0525-z. PMID: 25928287; PMCID: PMC4415291.
3 Nelson HD, Zakher B, Cantor A, et al. Risk factors for breast cancer for women aged 40 to 49 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156(9):635-648.
4 Pisano et al. NEJM 2005; 353: 1773.
5Buchberger W, Geiger-Gritsch S, Knapp R, Gautsch K, Oberaigner W. Combined screening with mammography and ultrasound in a populationbased screening program. Eur J Radiol. 2018 Apr;101:24-29
6 Up to 50% of breast cancers may be missed in extremely dense breasts. Kolb et al, Radiology, Oct 2002;225(1):165-75.
7 Compared to without contrast
8 J. Sung et al., Radiology 2019; 00:1–8
9 V. Sorin et al. American Journal of Roentgenology: W267-W274. 10.2214/AJR.17.19355
10 Data on file, GE Healthcare 2017
11 Data on file. GE Healthcare 2020
13 https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/dcpc/prevention/screening.htm
14 Data on file, GE Healthcare. 83% of patient assessed the exam as more comfortable than previous. IPSOS Patient Satisfaction Study sponsored by GE Healthcare, conducted with 315 patients across 2 sites in Europe
15 IPSOS Patient Satisfaction Study sponsored by GE Healthcare, conducted with 315 patients across 2 sites in Europe, out of whi ch 160 were offered the patient-assisted compression option, February 2017
16 FDA PMA P110006 summary of safety and effectiveness
17 Blumen, et al. Comparison of treatment costs for breast cancer by tumor stage, and type of service.
18 Sparano, JA, et al. N Engl J Med 2018; 379:111-121
19 Performance and Reading Time of Automated Breast US with or without Computer-aided Detection. Read More: https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiol.2019181816.
20 Interpretation Time Using a Concurrent-Read Computer-Aided Detection System for Automated Breast Ultrasound in Breast Cancer Screening of Women with Dense Breast Tissue (Yulei Jiang) Read More: https://www.ajronline.org/doi/10.2214/AJR.18.19516.
21 Mango et al. Should We Ignore, Follow, or Biopsy? Impact of Artificial Intelligence Decision Support on Breast Ultrasound Lesion Assessment. AJR, June 2020: 214: 1145-1452.
22Not available in all regions.
23 510(k) K103485
24 Daniaux et al. Arch Gynecol Obstet , 2015
25 iCAD labelling and user manual, DTM160 rev C. Reading times may vary based on the specific functionality of the viewing application used for interpretation
26 Kurland BF, Wiggins JR, Coche A, Fontan C, Bouvet Y, Webner P, et al. Whole-body characterization of estrogen receptor status in metastatic breast cancer with 16α-18F-fluoro-17β-estradiol positron emission tomography: meta-analysis and recommendations for integration into clinical applications. Oncologist. 2020;25(10):835-844.
27 Yang Z, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Xue J, Wang M, Shi W, et al. Can fluorine-18 fluoroestradiol positron emission tomography-computed tomography demonstrate the heterogeneity of breast cancer in vivo? Clin Breast Cancer. 2013;13(5):359-363.
28 Currin E, Peterson LM, Schubert EK, Link JM, Krohn KA, Livingston RB, et al. Temporal heterogeneity of estrogen receptor expr ession in bonedominant breast cancer: 18F-fluoroestradiol PET imaging shows return of ER expression. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2016;14(2):144-147.
29 Chae SY, Ahn SH, Kim S-B, Han S, Lee SH, Oh SJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and safety of 16α-[18F]fluoro-17β-oestradiol PET-CT for the assessment of oestrogen receptor status in recurrent or metastatic lesions in patients with breast cancer: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(4):546-555.
30 Amir E, Miller N, Geddie W, Freedman O, Kassam F, Simmons C, et al. Prospective study evaluating the impact of tissue confirmation of metastatic disease in patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(6):587-592.
31 Sundararajan L, Linden HM, Link JM, Krohn KA, Mankoff DA. 18F-fluoroestradiol. Semin Nucl Med. 2007;37(6):470-476.
32 Linden HM, Stekhova SA, Link JM, Gralow JR, Livingston RB, Ellis GK, et al. Quantitative fluoroestradiol positron emission tomography imaging predicts response to endocrine treatment in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(18):2793-2799.
33 Cardoso F, Fallowfield L, Costa A, Castiglione M, Senkus E, ESMO Guideline–– Working Group. Locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2011;22 Suppl 6:vi25-30.
34 Cerianna full prescribing information accessible here.

 July 30, 2024
July 30, 2024