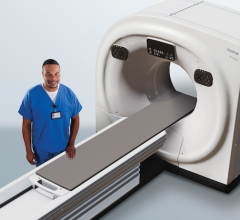
The Siemens Healthineers Somatom Pro.Pulse
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical imaging, computed tomography (CT) stands out as a cornerstone technology. Since its inception, CT has revolutionized diagnostic capabilities, offering detailed cross-sectional images of the human body. Over the years, advancements in CT technology have propelled the field forward, enhancing image quality, reducing radiation exposure and expanding clinical applications. Here is a look at five of the latest significant trends shaping the scope of computed tomography in medical imaging.
1. Cardiac CT
Perfusion CT and coronary CT angiography (CCTA) are instrumental in assessing tissue perfusion, vascular abnormalities and hemodynamic changes. Perfusion CT plays a crucial role in stroke evaluation, tumor characterization and assessment of vascular disorders. Advances in dynamic contrast-enhanced CT (DCE-CT) enable real-time assessment of tissue vascularity and pharmacokinetics, holding promise for personalized medicine and treatment monitoring.
CCTA had a large and noticeable presence on the RSNA23 exhibit hall floor, where Siemens Healthineers announced the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance of its Somatom Pro.Pulse, a dual-source CT scanner designed to be more affordable for a wide range of healthcare facilities. According to the company, the scanner combines the power and speed of dual-source CT technology with embedded artificial intelligence and user assistance features to deliver workflow efficiencies.
2. Photon-counting CT
Photon-counting CT represents a paradigm shift in CT detector technology. By directly counting individual photons rather than measuring their energy after interaction with scintillation materials, photon-counting detectors offer superior energy resolution, spatial resolution and multi-energy capabilities. These detectors facilitate spectral CT imaging, enabling enhanced material decomposition, virtual non-contrast imaging and improved image quality at reduced radiation doses.
Ultrahigh spatial resolution photon-counting detector CT improved assessment of coronary artery disease (CAD), allowing for reclassification to a lower disease category in 54% of patients, according to a recent study published in Radiology. The study found that the technology has the potential to improve patient management and reduce unnecessary interventions, however its co-author Tilman Emrich, MD, attending radiologist at the University Medical Center Mainz in Germany, and assistant professor of radiology at the Medical University of South Carolina, stated it is important to note that the findings were from a simulation study, and further validation in real-world comparisons is needed.
3. AI Integration and Radiomics
The convergence of radiomics and AI is reshaping CT imaging analysis. Radiomics extracts quantitative data from medical images to characterize tissue properties and predict clinical outcomes. AI algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns, classify abnormalities and assist in diagnostic decision-making by detecting abnormalities and quantifying disease burden. Integrating radiomics and AI into CT interpretation enhances diagnostic accuracy, enables predictive modeling, and facilitates personalized medicine approaches and treatment plans.
4. Dose Reduction
With increasing concerns about radiation exposure in medical imaging, there is a continued emphasis on developing techniques to reduce radiation dose in CT imaging without compromising diagnostic accuracy. Innovations such as adaptive dose modulation, optimized scanning protocols and AI-driven dose reduction algorithms are helping to minimize radiation exposure while maintaining image quality and diagnostic confidence.
5. Portable and Point-of-care CT
The integration of CT into point-of-care settings is a burgeoning trend, driven by the demand for rapid and accessible diagnostic imaging. Portable and compact CT scanners are being developed for use in emergency departments, intensive care units and remote healthcare facilities. These systems enable timely imaging, facilitating prompt diagnosis and treatment decisions. Point-of-care CT also holds promise for applications in resource-limited settings and telemedicine. A variety of medical imaging companies offer portable CT options.
NeuroLogica’s FDA-approved head-to-toe trauma imaging solution, the BodyTom 64 point-of-care mobile CT scanner, is designed to enhance the user experience and improve clinical workflows through revisions to both the software and the data acquisition system. The scanner has indications for both pediatric and adult imaging, and can be used for a variety of needs, bringing the power of innovative imaging to patients’ bedsides safely and efficiently.
The Imaging Evolution
Computed tomography continues to evolve and is driven by technological innovations and clinical demands. From advancements in image reconstruction algorithms to the integration of photon-counting detectors, the landscape of CT imaging is marked by continuous progress. These trends hold the promise of improving diagnostic accuracy, reducing radiation exposure and expanding the clinical utility of CT across diverse medical specialties. As we navigate the future of medical imaging, computed tomography remains at the forefront, shaping the way we visualize and understand the human body.
View the Computed Tomography Systems Comparison Chart here

Melinda Taschetta-Millane is Editorial Director for Imaging Technology News, and is an award-winning medical editor, including three Jesse H. Neal Awards, the most prestigious editorial honor in the field of journalism. She has led the editorial direction of ITN for the past 13 years, and has extensive experience covering the medical field, focusing on radiology, radiation oncology, medical information technology, cardiology and women's health issues.


 August 09, 2024
August 09, 2024