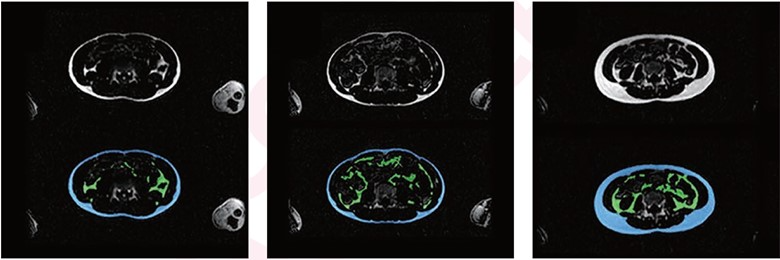
Automated abdominal adipose tissue segmentation into SAT, VAT via Dixon MRI in different children. In each image, top and bottom images represent fat-only images without (top) and with (bottom) segmentation. Blue area denotes SAT, and green area denotes VAT. Left, center, and right represent three children with varying body sizes and varying amounts of abdominal SAT and VAT. (Left) 13-year-old underweight girl. Dice similarity coefficient and volumetric similarity are for SAT, 0.94 and 0.99, and for VAT are 0.85 and 0.92. (Center) 13-year-old underweight boy. Dice similarity coefficient and volumetric similarity are for SAT, 0.91 and 0.96, and for VAT, 0.82 and 0.90. (Right) 13-year-old normal-weight girl. Dice similarity coefficient and volumetric similarity are for SAT, 0.97 and 0.98, and for VAT are 0.86 and 0.95.
August 18, 2023 — According to an accepted manuscript published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), an automated model could enable large-scale studies in adolescent populations that investigate abdominal fat distribution on MRI, as well as associations of fat distribution with clinical outcomes.
Noting that a global increase in childhood obesity has created the need to accurately quantify body fat distribution, “we trained and evaluated the 2D-CDFNet model on Dixon MRI in adolescents,” wrote co-first author Tong Wu, MD, from the department of radiology and nuclear medicine at Erasmus MC University Medical Center in The Netherlands.
Watch Dr. Wu discuss training and evaluating this 2D-CDFNet model on Dixon MRI in adolescents.
Embedded within the Generation R Study—a prospective population-based cohort study in Rotterdam—Wu et al.’s AJR manuscript included 2,989 children (mean age, 13.5 years; 1,432 boys, 1,557 girls) who underwent investigational whole-body Dixon MRI upon age 13. A competitive dense fully convolutional network (2D-CDFNet) was trained from scratch to segment abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) and visceral adipose tissue (VAT) from Dixon images. The model underwent training, validation, and testing in 62, 8, and 15 children, respectively, selected via stratified random sampling with manual segmentation for reference. The AJR authors then assessed the performance of their segmentation using Dice similarity coefficient and volumetric similarity. Two independent observers visually evaluated automated segmentations in 504 children, selected by stratified random sampling, as well as scoring undersegmentation and oversegmentation (scale of 0-3).
Ultimately, this model for automated SAT and VAT segmentation from Dixon MRI showed strong quantitative performance (Dice coefficients and volumetric similarity relative to manual segmentations: range, 0.85-0.98) and qualitative performance (best possible visual score of 3/3 by two independent observers in 95-99% of assessments).
For more information: www.arrs.org


 December 10, 2025
December 10, 2025 









