If you enjoy this content, please share it with a colleague
RELATED CONTENT
Despite concerns to the contrary, very little of the variation in Emergency Department (ED) imaging utilization is attributable to physician experience, training or gender, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
The distribution of white matter brain abnormalities in some patients after mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI) closely resembles that found in early Alzheimer’s dementia, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
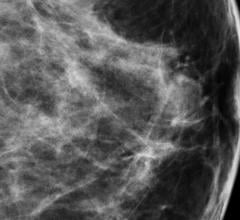
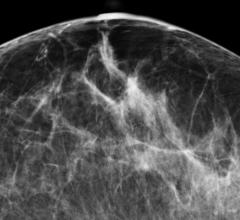
December 18, 2012 — The addition of 3-D breast imaging, or tomosynthesis, to standard digital mammography significantly increases radiologists’ diagnostic accuracy while reducing false positive recall rates, according to the results of a multicenter study published in Radiology.
December 13, 2012 — Researchers reviewing the records of approximately 250,000 women enrolled in an integrated healthcare delivery system found that increased CT (computed tomography) utilization between 2000 and 2010 could result in an increase in the risk of breast cancer for certain women, including younger patients and those who received repeat exams.
A new three-dimensional (3-D) digital mammography technique has the potential to significantly improve the accuracy of breast cancer screening, according to a study published in Radiology.
The Radiological Society of North America's (RSNA) 98th annual scientific assembly is set for Nov. 25-30, 2012, at McCormick Place in Chicago. The event is the largest radiology meeting in the world, with about 60,000 expected to attend. It includes nearly 3,000 educational sessions as well as hundreds of vendors displaying as part of the technical exhibition.
October 4, 2012 — New research from the Netherlands shows that the switch from screen film mammography (SFM) to digital mammography (DM) in large, population-based breast cancer screening programs improves the detection of life-threatening cancer without significantly increasing detection of clinically insignificant disease. Results of the study are published online in the journal Radiology.
August 29, 2012 — New magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) research shows that changes in brain blood flow associated with vein abnormalities are not specific for multiple sclerosis (MS) and do not contribute to its severity, despite what some researchers have speculated. Results of the research are published online in the journal Radiology.
August 17, 2012 — Researchers at the Mayo Clinic say a common condition called leukoaraiosis, made up of tiny areas in the brain that have been deprived of oxygen and appear as bright white dots on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, is not a harmless part of the aging process, but rather a disease that alters brain function in the elderly. Results of their study are published online in the journal Radiology.
July 30, 2012 — A buildup of sodium in the brain detected by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be a biomarker for the degeneration of nerve cells that occurs in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.


 July 01, 2013
July 01, 2013