Over the past several years, technological advancements have driven the development of more precise and targeted radiation therapy techniques, improved treatment outcomes and minimizing side effects. The market trend is moving toward advanced radiation therapy techniques, such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) and proton therapy, all which offer enhanced precision and better conservation of healthy tissues. There is a rising demand for integrated oncology solutions that combine radiation therapy with other treatment modalities like surgery and chemotherapy, as well.
According to recent data from Market.us, the global radiation oncology market size is currently estimated to be worth around $8.2 billion, growing to $19.2 billion in 2032, which is a CAGR growth of 9.1%. Seeing these numbers, it comes as no surprise that radiation oncology played a growing role at the Radiological Society of North America 109th Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting (RSNA23). Here are some of the significant trends discussed on this year’s show floor.
Personalized Medicine
There is a growing emphasis on personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s unique genetic profile and tumor characteristics. This approach aims to optimize treatment outcomes while minimizing side effects.
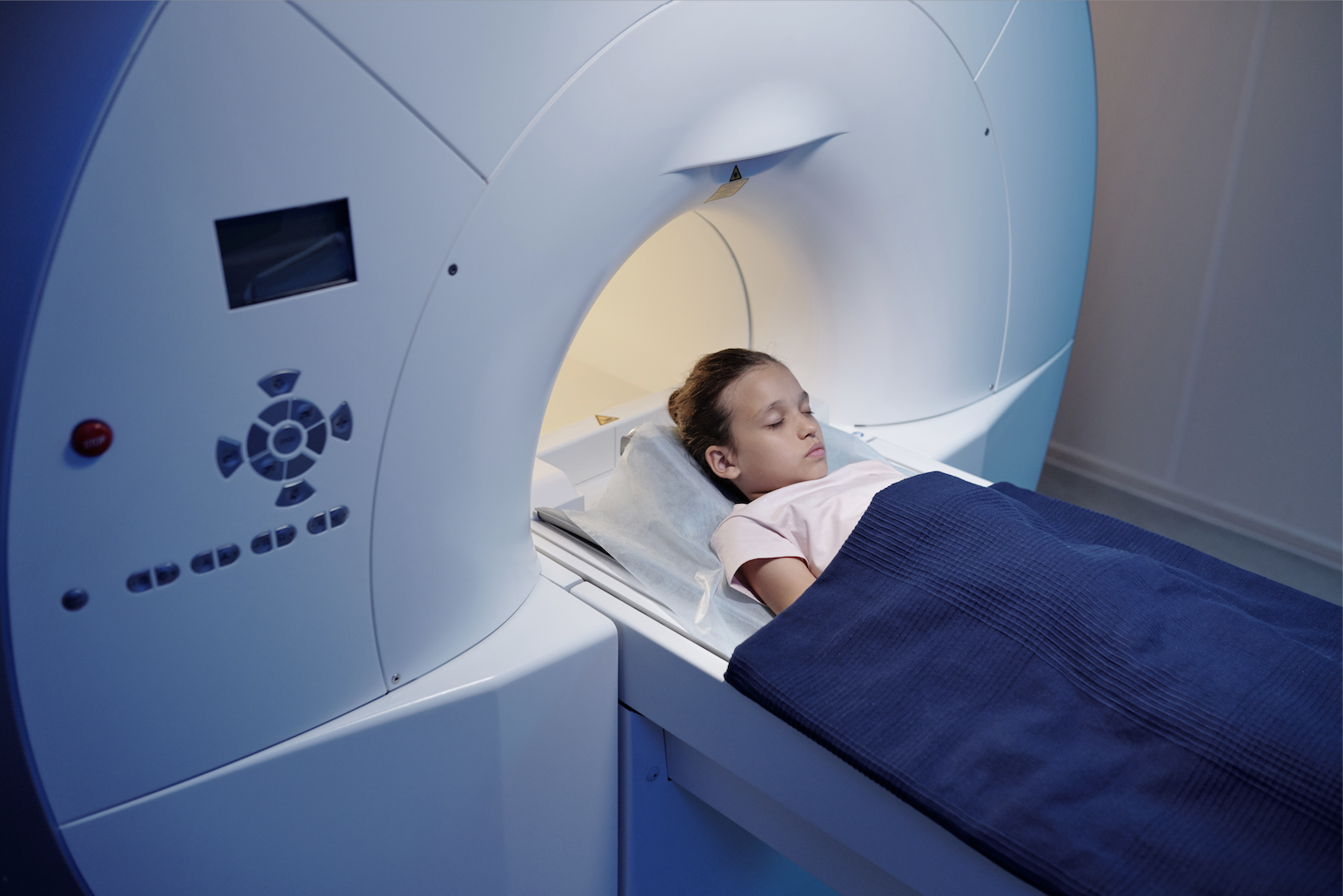
The Radiation Oncology Program at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles (CHLA) is one such example, and one of only a few facilities in the country to care exclusively for children. The team combines extensive expertise with advanced technology to deliver precision treatments, which aim to maximize cure while minimizing late effects.
CHLA Radiation Oncologist Kenneth Wong, MD, and Medical Physicist Arthur Olch, PhD, FAAPM, work alongside the Children’s Oncology Group consortium to design and implement pediatric radiation clinical trials across the country. In a written statement last December, Olch and Wong, together with Eric Lin Chang, MD, professor and chair of radiation oncology at USC, shared innovations that are impacting pediatric radiation care today.
“We’re entering an era of personalized medicine on all fronts, including pediatric radiation oncology,” said Chang. “We’re going to be refining patient selection based on molecular markers that predict the disease behavior and can help us determine how aggressive or intensive our treatments should be.”
As an example, CHLA is participating in a Children’s Oncology Group clinical trial that is investigating whether radiation doses can be reduced in patients who have a favorable genetic profile for certain cancers.
“The ultimate goal is to select the patients who don’t need radiation therapy at all,” Chang stressed. “That’s difficult to do, and it needs more study, but the hope is that more molecular markers will be available to help us make these decisions and personalize care for each child.”
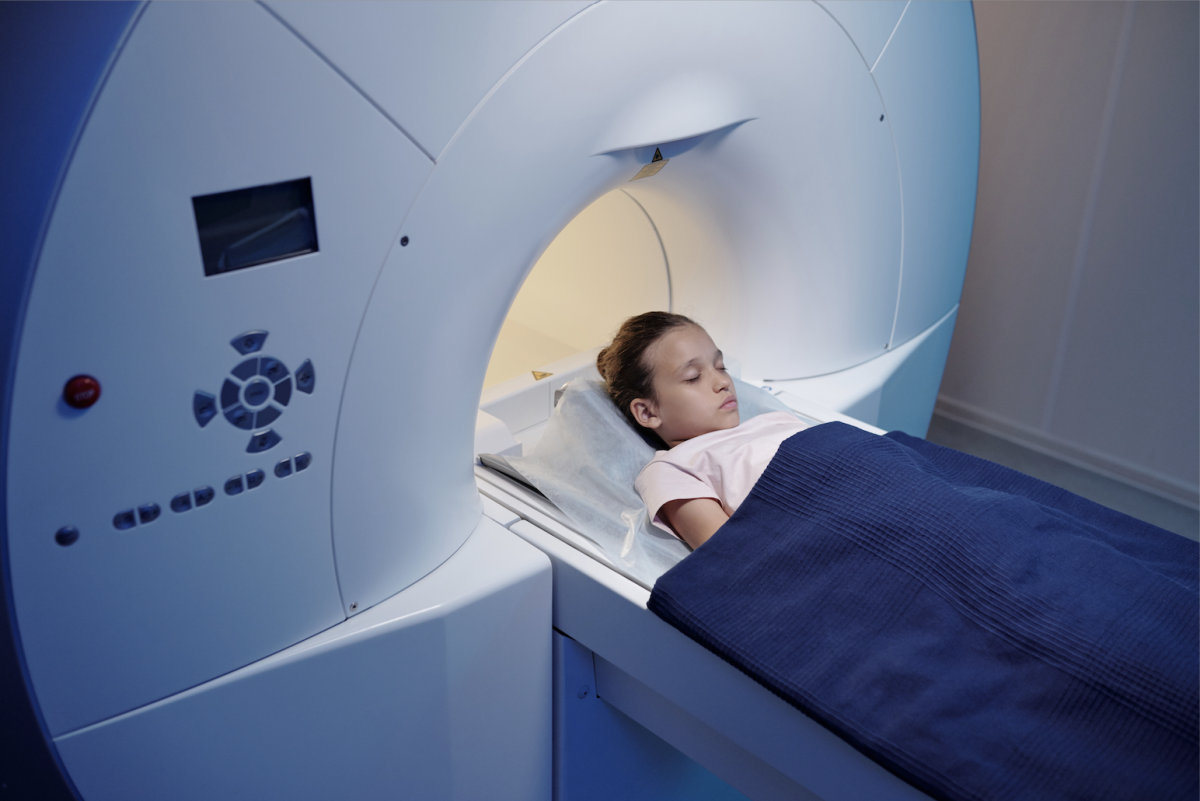
The growing emphasis on personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s unique genetic profile and tumor characteristics aims to optimize treatment outcomes while minimizing side effects, and this technology is being used in pediatric oncology. Getty Images
Recently, iCAD, Inc., a global medical technology leader in innovative cancer-detection solutions, and CancerIQ, a precision cancer prevention platform streamlining provider workflows and activating high-risk patients, announced a new partnership to create a best-in-class breast healthcare solution. The companies report the partnership will provide a seamless way to uniquely inform physicians and patients of cancer risk — which includes lifetime, genetic and AI-detected near-term risk — identify breast cancer at earlier stages when treatments will work best, and increase patient adherence to personalized care plans.
iCAD noted that these solutions will combine elements of its artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled ProFound Breast Health Suite with CancerIQ’s software and services. This will reportedly give users a 2.4x more accurate prediction of breast cancer risk, by combining AI-informed 1- or 2-year risk with lifetime risk, as well as a unique care management and patient activation workflow solution.
“This partnership will streamline how patients and physicians use our collective health data to schedule preventive screenings and manage breast health care in a way that will save lives,” said Dana Brown, president and CEO of iCAD, in the same statement. “We look forward to a long-term relationship with CancerIQ that will create meaningful, actionable information in terms of proactive and personalized care benefiting both medical providers and the patients they serve.”
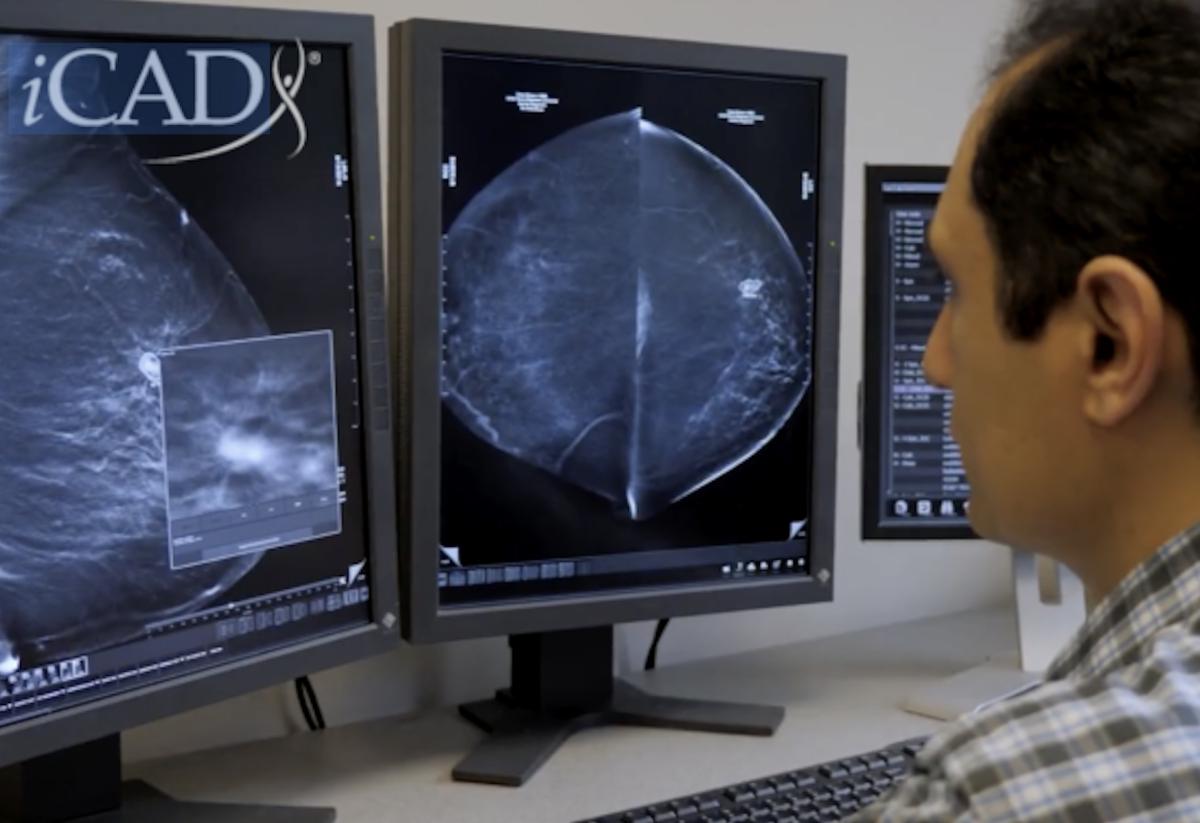
iCAD and CancerIQ recently announced a new partnership to create a best-in-class breast healthcare solution. Image courtesy of iCAD
Value-based Care
Healthcare systems have increased their focus on providing value-based care, helping to improve patient outcomes while managing costs effectively as efforts are made to enhance treatment efficacy while reducing unnecessary procedures and expenses.
Today, prostate cancer and Alzheimer’s Disease are prevalent, and GE HealthCare’s AIR technologies that are incorporated in the Signa PET/MR Air scanner help directly impact these, and other challenging diseases, that are difficult to diagnose and treat.
The combination of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) targeted positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracers with GE’s high sensitivity PET and the anatomical precision of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the Signa PET/MR Air holds the potential to help clinicians make a more precise diagnosis and staging/re-staging of prostate cancer, according to the company.
The recent approval of PET amyloid tracers and new Alzheimer’s treatments require imaging of patients with MRI and PET. Signa PET/MR Air offers a sensitive time-of-flight (ToF) PET detector in a PET/MR, helping to enable clinicians achieve early diagnosis, track disease progression and detect adverse side effects in a single scan. According to the company, the system delivers deep learning-based MRI image reconstruction with AIR Recon DL, helping to ensure both improved image quality and up to 50% reduction in scan time.
MotionFree Brain PET on the Signa PET/MR Air addresses and manages patient movement during imaging, without external tracking devices. Images affected by motion on the Signa PET/MR Air can be corrected even after the patient has left the scanner.
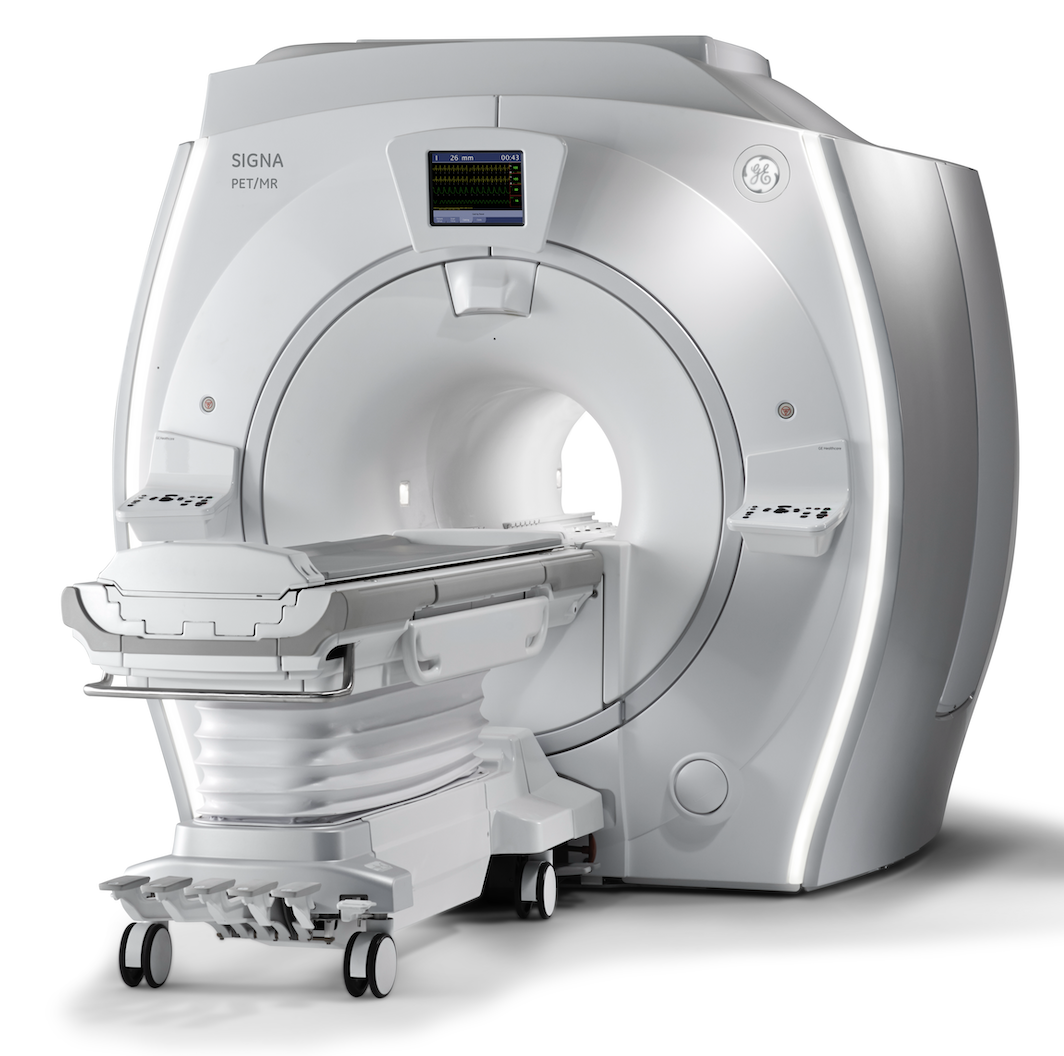
GE HealthCare’s AIR technologies that are incorporated in the Signa PET/MR Air scanner help directly impact prostate cancer, Alzheimer’s, and other challenging diseases. Image courtesy of GE HealthCare
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming more integrated into everyday healthcare, and machine learning is being utilized to analyze complex data, aid in treatment planning, automate tasks and improve treatment outcomes by assisting in decision-making processes, just to name a few benefits.
Philips is leveraging the power of AI-assisted technology in its MR SmartSpeed image reconstruction software. In a newly announced partnership, Philips and Quibim are working on an integrated solution that includes Quibim’s AI-based QP-Prostate software to help automate real-time prostate gland segmentation in MRI images. According to the company, this will generate meaningful quantitative insights, and standardize MRI prostate exam reporting. When combined with Philips’ AI-based MRI imaging techniques, the solution’s goal is to provide clinicians with the speed and precision needed to deal with the growing number of patients in need of MRI exams, and to proceed with these exams with diagnostic confidence, personalized treatment and ultimately better outcomes.
“This collaboration with Quibim is the latest example of our commitment to build an AI ecosystem into our diagnostic imaging portfolio to help detect conditions like cancer earlier, improve the rate of accurate first-time-right diagnosis and streamline hospital operations to provide better care at lower costs,” said Ruud Zwerink, general manager of MR at Philips, in a written statement centered around RSNA23. “The collaboration with Quibim will ultimately be extended to address other forms of cancer beyond prostate, where there is a need to improve efficiency and mitigate staff shortages while delivering high-quality oncology care to an increasing number of patients.”
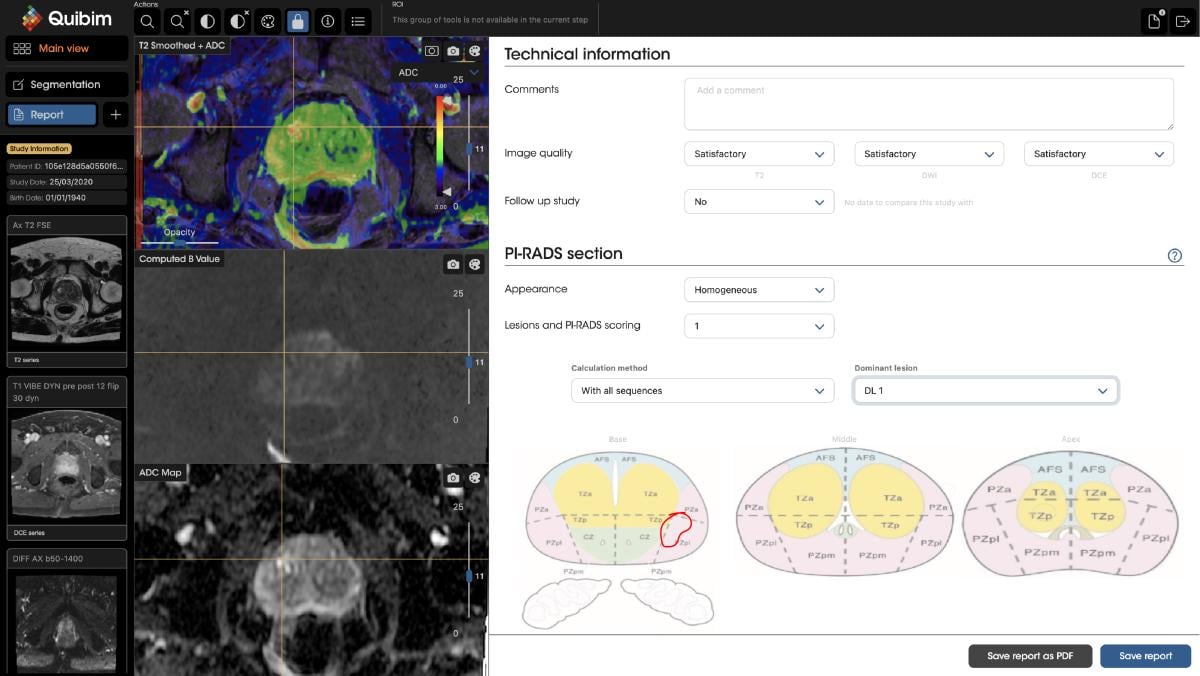
Quibim’s QP-Prostate is an AI-powered solution designed to streamline radiologists’ workflows. Image courtesy of Quibim
Also, Pixyl, a French medtech company specializing in AI-powered MRI solutions to improve patient care, recently announced FDA 510(k) clearance for Pixyl.Neuro, its next-generation AI software for brain MRI analysis. This solution automatically analyzes brain MRI images to support rapid detection, early diagnosis and objective monitoring of neurological disorders. According to the company, it leverages generative AI technology to ensure robust performance in real-world practice.
New Players to the Field
TeleDaaS, a dosimetry-as-a-service provider, made its debut at the RSNA23. The company specializes in delivering clinical-grade, precision-based dosimetry analysis and treatment plans to clinical research organizations (CROs) and pharmaceutical manufacturers, and is designed to provide highly scalable, best-in-class dosimetry services that integrate with existing imaging workflows. This, in turn, helps to transform cancer treatment research and development.
“We are launching TeleDaaS to arm those researching and developing breakthrough cancer treatments with the technology and services needed to usher in the next generation of precision cancer therapies,” said TeleDaaS Chief Medical Officer Mark Crockett, MD, in a written announcement released during RSNA23. “Radiopharmaceuticals are revolutionizing modern cancer treatment and precision dosimetry is a crucial component of this advanced therapy. By marrying proven technology and expertise in personalized dosimetry, coupled with the accessibility and scalability of telemedicine, TeleDaaS is committed to pushing the boundaries of what is possible in this field.”
At TeleDaaS, a team of leading dosimetry practitioners leverage proprietary software from Mirada Medical, LTD, which integrates with standard imaging technology, to support clinical research organizations in clinical trial design, execution and the development of new targeted radiation therapies. TeleDaaS’s platform is highly scalable for clinical trials and offers CROs and pharmaceutical companies flexibility with regard to hiring in-demand dosimetrists.
“We are seeing exciting developments in the field of dosimetry to keep up with the rapid expansion to different radioisotopes and corresponding dosimetric requirements,” said Jessica Guarnaschelli, MD, a radiation oncologist who uses the platform. “I anticipate that the benefit of radiopharmaceuticals will be maximized by combining radiopharmaceutical therapies with a vast array of other agents including immunotherapies, chemotherapeutics, radiosensitizers and radioprotectors. This is already showing promise with several ongoing trials of approved and developmental radiopharmaceuticals. With the advancements in this field, TeleDaaS enters the market at a crucial time when the science and the technology align.”
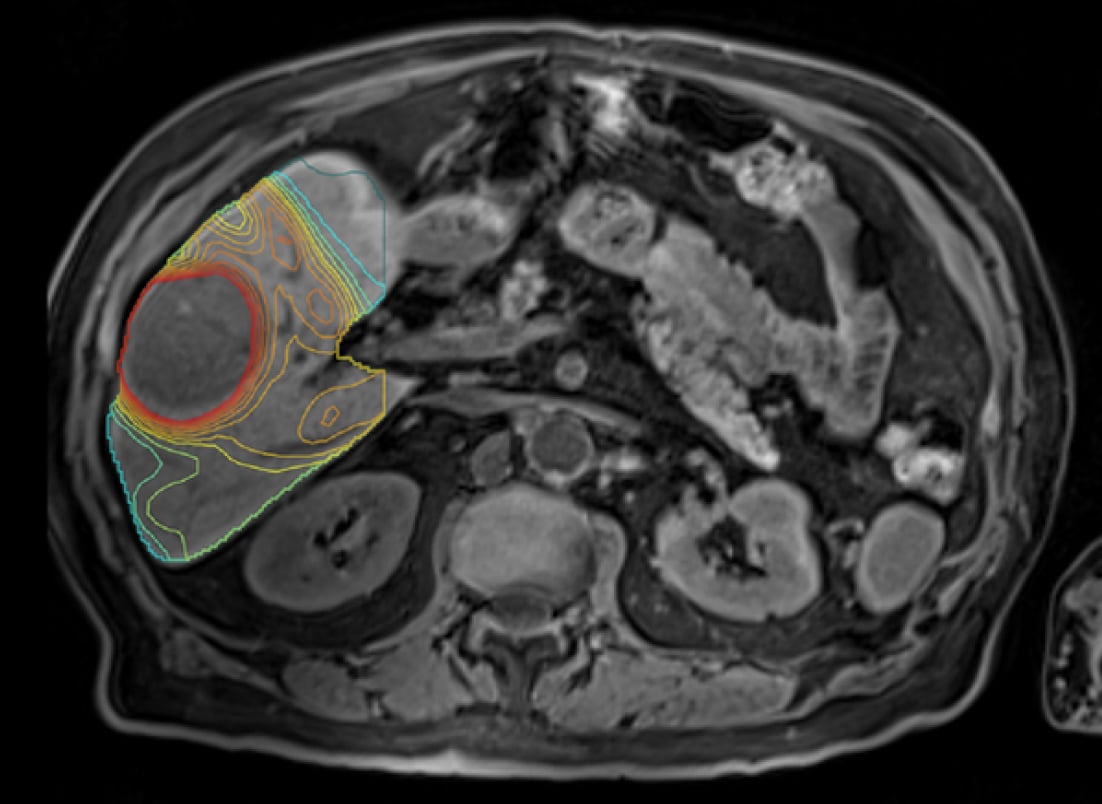
A team of leading dosimetry practitioners at TeleDaaS leverage proprietary software from Mirada Medical, which integrates with standard imaging technology, to support clinical research organizations in clinical trial design, execution and the development of new targeted radiation therapies. Image courtesy of TeleDaaS
Additional Noteworthy Highlights
Other trends and news of note showcased during RSNA23 included:
•Clinical research and trials. Ongoing clinical trials are exploring new treatment modalities, combinations of therapies and innovative approaches to radiation oncology. As a result, these research efforts drive the development of novel techniques and contribute to improved patient care.
•Technological advancements. Radiation therapy has seen significant advancements in technology, including more precise delivery systems like stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT), proton therapy and intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). These technologies enable more targeted treatment, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
•Integration of immunotherapy. Combining radiation therapy with immunotherapy is a promising avenue in cancer treatment. This combination has shown potential for enhancing the immune system’s response against cancer cells, leading to improved outcomes in certain cancers.
•Reducing treatment duration. Hypofractionation, which involves delivering higher doses of radiation over fewer sessions, is gaining traction. This approach aims to shorten treatment duration while maintaining effectiveness.
•Patient-centered care. There’s a growing focus on improving the overall patient experience during radiation therapy. Efforts are being made to reduce treatment-related side effects, enhance supportive care, and involve patients in shared decision-making.
•Challenges in access and equity. Disparities in access to radiation therapy services exist due to various factors, including geographical location, socioeconomic status and healthcare infrastructure. Efforts to address these disparities and improve access to quality care are both increasing and ongoing.
•Workforce and training. There is a need to ensure an adequate workforce equipped with the skills to leverage evolving technologies and meet the increasing demand for radiation oncology services. Training programs and ongoing education are essential to support the workforce in delivering high-quality care.
•Telemedicine and remote monitoring. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine and remote monitoring in radiation oncology. These technologies facilitate consultations, follow-ups and monitoring, enhancing both patient convenience and access to care.
The radiation oncology market continues to see advancements and trends that further shape this growing field, as was evidenced at RSNA23. Techniques like stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) and proton therapy have gained traction due to their precision in targeting tumors while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms have revolutionized treatment planning, enabling personalized radiation therapy plans and more accurate dosage delivery. Immunotherapy in combination with radiation has emerged as a promising avenue, leveraging the immune system to enhance the effects of radiation on cancer cells. And finally, there is a growing focus on patient-centered care, emphasizing quality of life during and after treatment, leading to comprehensive supportive care measures and survivorship programs within radiation oncology.


 December 04, 2025
December 04, 2025 









