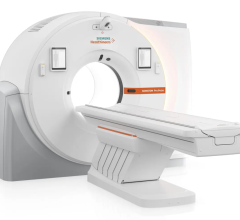
The Siemens Healthineers 3T Magnetom Cima.X. Faster scan time with Deep Resolve for TSE outruns motion and substantially shortens the prostate exam. Image courtesy of Siemens Healthineers
The world of medical imaging is marking a significant milestone in 2023: the 50th anniversary of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI is an efficient diagnostic procedure which uses magnetic radio waves to take internal medical images of the body, and is used to investigate and/or diagnose conditions that affect soft tissue. It assists in identifying diseases related to spine lesions, tumors, and stroke impacting the area of blood vessels and brain. The increasing prevalence of these diseases is expected to play an important role in the market growth.
According to Grand View Research in its Market Analysis updated June 2023, the global magnetic resonance imaging market size was valued at $5.26 billion in 2022 and is estimated to be at $9.1 billion by 2030. Grand View Research further forecasts a CAGR of 6.8% over the forecast period 2023-2030.
Three key factors are identified as drivers boosting the market’s growth — integration of artificial intelligence in MRI, technological innovations and the growing incidence of chronic conditions.
North America dominated the global market, capturing over 37% in 2021, noted Grand View Research. Increasing incidence of chronic diseases (breast cancer, cardiovascular disorders, neurological disorders) is creating a demand for imaging analysis, report analysts, who anticipate the region is expected to maintain its dominance in the forecast period.
Rapidly growing European countries, such as the UK, France and Germany, are showing increased demand for advanced diagnostic imaging modalities. The report forecasted that Asia Pacific will experience the fastest growth due to an increasing geriatric population and growing demand for advanced modalities.
About Wide Bore
As summarized by Intermountain Medical Imaging, despite all the benefits of using MRIs, one of the drawbacks has traditionally been the machine’s narrow opening and sides. Offering a wide bore MRI helps address these patient concerns, which often prevent people from obtaining the testing they need. On a standard MRI, the bore size is roughly 60 centimeters in diameter or under two feet. With large-bore MRI machines, the opening is 70 centimeters. IMI notes this additional space makes a huge difference in better accommodating patients and making them more comfortable.
Five benefits of utilizing wide bore MRIs, writes IMI, are: Better accommodations for larger patients; reduced discomfort; overall broader testing and treatment by increasing number and types of clients served; improved image quality; and more efficient testing, noting fewer retakes or errors, cutting the time patients need to remain in the scanner.
Brain and neurological imaging held the largest share of the MRI systems market in 2022, holding more that 24%, while the breast imaging segment is expected to grow to due increasing prevalence of breast cancers in women. MRI is notably becoming preferred method for spinal and musculoskeletal imaging.
The hospital segment held the largest share of around 39% in 2022. Increasing applications of rapid MRI (rMRI) in trauma and emergency care centers, and the rising number of MRI installments in teaching hospitals, is expected to fuel the segment growth. The imaging centers segment is expected to experience the fastest growth rate during the forecast period.
Latest Innovations
Collaboration between vendors and engineering departments at colleges across the United States are fueling MRI advancements.
For its part, Siemens unveiled the 3T Magnetom Cima.X in December, 2022, at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The scanner offers unprecedented technical performance features when compared to conventional whole-body MRI systems in place now. A developmental scanner, the Cima is not yet commercially available. According to a Texas A&M Today article (January 2023 by Adrena Dow, of Texas A&M School of Engineering Medicine), the scanner was inspired by the School of Engineering Medicine’s inaugural Dean Roderic Pettigrew, PhD. The feature details how Pettigrew — a former and founding director of NIH’s National Institute for Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering — made the proposal to Siemens Healthineers. The new technology is being developed to detect threats early and help prevent severe consequences, such as seeing coronary or vascular diseases before a heart attack or stroke, or identifying prostate cancer in its earliest stage before a biopsy.
“This is an exciting development in the field of whole-body MRI, and its potential to improve clinical care and research is just beginning to be explored,” Pettigrew said.
In another key development, the National Institutes of Health has awarded University of Arizona researchers a $2 million High-End Instrumentation grant to help purchase an advanced 3Tesla MRI instrument for studying the human brain, according to a June 2023 news update from University of Arizona compiled by Emily Dieckman with the College of Engineering. The university will be among the first US institutions to receive the new Siemens Healthineers model. The system, scheduled for delivery this fall, will have advanced hardware that can produce clearer and more comprehensive images of the brain with greater speed.
Leading the effort is Ted Trouard, PhD, professor emeritus of biomedical engineering in the College of Engineering, professor of medical imaging in the College of Medicine – Tucson, principal grant investigator, and a professor at the Evelyn F. McKnight Brain Institute, and the BIO5 Institute, with whom he collaborated on the grant proposal.
Detailed specifications of multiple wide bore MRI systems from leading market players are shown in ITN’s Comparison Chart, exhibiting the promise MRI technology offers as it marks its fifth decade.
View the MRI Wide Bore Systems Comparison Chart
Related MRI Content:
MRI turns 50: Expert Brad Sutton Explains its History and Role in Understanding the Aging Brain

 August 06, 2024
August 06, 2024