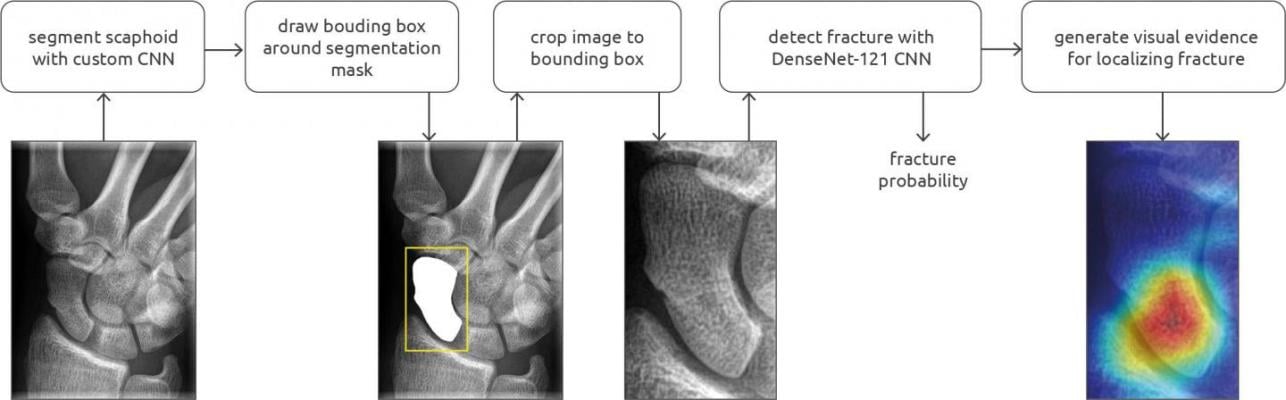
Overview of the scaphoid fracture detection pipeline, which consisted of a segmentation and detection convolutional neural network (CNN). A class activation map is calculated and visualized as a heatmap for fracture localization. Image courtesy of the Radiological Society of North America
April 28, 2021 — An automated system that uses artificial intelligence (AI) is effective at detecting a common type of wrist fracture on X-rays, according to a study published in the journal Radiology: Artificial Intelligence. Researchers said the AI-derived algorithm could help speed diagnosis and allow earlier treatment.
Scaphoid fractures are injuries to one of the small bones of the wrist that typically occur when people try to break a fall with their hands. They comprise up to 7% of all skeletal fractures. Prompt diagnosis is important, as the fracture may fail to heal properly if untreated, leading to a host of problems like arthritis and even loss of function.
Conventional X-ray is the imaging technique of choice for diagnosing scaphoid fractures, but it is often limited by overlap of the scaphoid with the surrounding bones of the wrist. Variations in wrist positioning and X-ray technique can also limit the visibility of fractures.
"Consequently, scaphoid fractures can be overlooked during initial X-ray examinations," said study lead author Nils Hendrix, a Ph.D. candidate at the Jeroen Bosch Hospital and Jheronimus Academy of Data Science in the Netherlands.
Hendrix and colleagues recently studied a system that could aid radiologists in detecting these common fractures. The system is based on deep learning with a convolutional neural network, a sophisticated type of AI that is capable of discerning subtle patterns in images beyond the capabilities of the human eye.
While previous research found that a convolutional neural network was inferior to human observers at identifying scaphoid fractures on X-rays, the new study used larger datasets and further algorithm refinements to improve detection. It also employed class activation maps, which are AI tools that help users understand what region of the image is influencing the network's predictions.
The researchers used thousands of conventional X-rays of the hand, wrist and scaphoid to develop the system. They tested it on a dataset of 190 X-rays and compared its performance to that of 11 radiologists.
The system had a sensitivity of 78% for detecting fractures with a positive predictive value of 83%, which refers to the likelihood that patients the AI identifies as having a fracture really do have one. Analysis showed that the system performed comparably to the 11 radiologists.
The system has significant potential in clinical use, Hendrix said. It could reduce the incidence and costs of additional imaging exams and unnecessary therapy, speed up diagnosis and allow earlier treatment.
"The system may be able to assist residents, radiologists or other physicians by acting either as a first or second reader, or as a triage tool that helps prioritize worklists, potentially reducing the risk of missing a fracture," Hendrix said.
Such assistance could prevent delayed therapy and reduce complications that may lead to a subpar clinical outcome, according to Hendrix.
"The convolutional neural network may also reduce unnecessary wrist immobilization, performed out of precaution, in more than half of the patients with clinical suspicion for having a scaphoid fracture," he said.
The class activation maps were found to overlap with fracture lines in the scaphoid, suggesting they could be used for localizing potential fractures.
Hendrix and colleagues plan to expand the scaphoid fracture detection system so that it can combine multiple X-ray views for its predictions. They are also conducting an experimental study in which radiologists are asked to identify scaphoid fractures on X-rays with and without the aid of the fracture detection system.
The researchers hope to extend the system to fracture detection in other bone structures.
For more information: www.rsna.org




 April 17, 2025
April 17, 2025