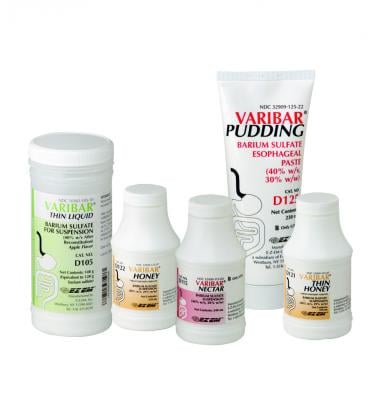
August 5, 2019 — Bracco Diagnostics Inc. announced U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for Varibar Thin Liquid (barium sulfate) for oral suspension, which is indicated for modified barium swallow (MBS) studies. The contrast agent is used to detect and assess the type and severity of swallowing disorders also known as dysphagia.
In the U.S., approximately 13 million (1 in 25) Americans suffer from dysphagia.1 Dysphagia varies in severity and can be caused by a number of conditions and diseases, such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, dementia, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, and treatment of head and neck cancer or trauma.1 The most common complications are aspiration pneumonia, malnutrition and dehydration.2 Aspiration pneumonia is a subset of pneumonia caused by inhalation of substances such as liquid and/or food into the lungs when the swallowing mechanism does not function properly. It requires hospitalization and is associated with 10 percent in-hospital mortality and high hospitalization cost, estimated at approximately $30,000 per case.3
An MBS study is performed by a team comprised of a speech language pathologist (SLP) and a radiologist to identify issues with a patient's swallowing mechanism. During an MBS, the patient swallows products with different thicknesses containing a barium X-ray contrast agent, while the radiologist takes fluoroscopic X-ray images.
Varibar Thin Liquid (barium sulfate) oral suspension requires reconstitution prior to use.
For more information: www.imaging.bracco.com
References
1. Bhattacharyya N. The prevalence of dysphagia among adults in the United States. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 2014; 151: 765–769
3. Wu C-P., Chen Y-W., Wang M-J., et al. National Trends in Admission for Aspirational Pneumonia in the United States, 2002-2012; Annals ATS 2017, 14: 874-879

 July 30, 2024
July 30, 2024