June 4, 2009 - Agfa HealthCare released IMPAX 6.4, the latest version in the IMPAX PACS product line, which delivers new features and tools to aid users in managing complex multiseries studies that are the rule rather than the exception in today's imaging technology.
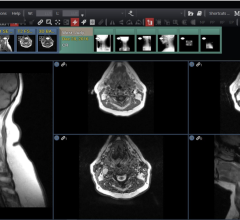
Agfa HealthCare's IMPAX 6.4 offers an improved navigation workflow for large CT and MR datasets for radiologists, clinicians and other healthcare professionals, introducing new workflow features that include 'Active Target', a tool that simplifies multi planar, cross sectional navigation and replaces the traditional 'stack' navigation to view areas of interest in all planes simultaneously. IMPAX 6.4 also includes the 'Auto Link' feature which automatically links 'like series' within one study to make navigation through numerous series more efficient. To enact comparative navigation across multiple studies, IMPAX 6.4 provides cross study series linking. All of these features employ graphical indications to ensure users are aware of where they are in a particular series when navigating. To help manage the distribution of results for large studies, IMPAX 6.4 introduces a 'Key Image workflow' that automates the presentation of those key images via clinical views and through EPR applications.
In addition to these navigation tools, IMPAX 6.4 introduces IMPAX Volume Viewing to assist users in reading volumetrically acquired datasets such as multi-slice CT studies or 3D MR acquisitions. IMPAX Volume Viewing will be included as the default MIP/MPR application with IMPAX 6.4, supporting standards viewing as well as curved MPR and a study comparison workflow.
IMPAX 6.4 further introduces new features for simplified worklist management and a new study claim workflow to allow users to manage the assignment and ownership of particular studies for managed reporting workflow in larger institutions.
The IMPAX 6.4 release also continues to offer the tight integration of reporting tools and workflows to provide efficient and effective voice dictation to the desktop. User communications will greatly benefit with the introduction of voice-based study comments to simplify the delivery of urgent finding and facilitate improved communications between clinicians.
For more information: www.agfa.com


 July 25, 2024
July 25, 2024