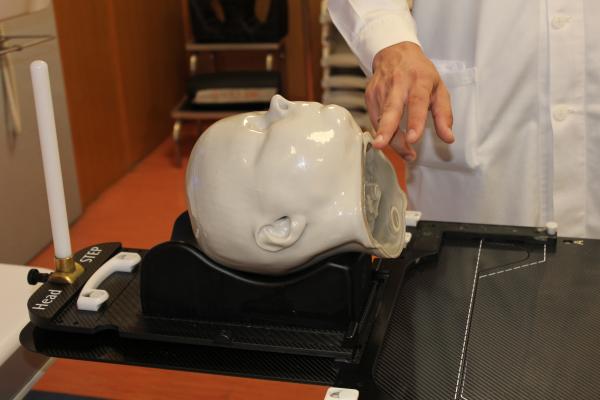
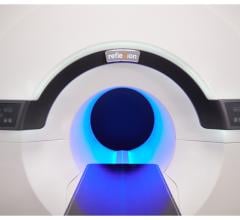
RTsafe’s PseudoPatient that is used to verify radiotherapy dosage and accuracy ahead of patient treatment.
March 16, 2023 — RTsafe, a leading provider of quality assurance products and services in stereotactic radiosurgery, announces that Spain’s Fundación Instituto Valenciano de Oncología (IVO) has conducted its first simulated therapy for brain metastases using PseudoPatient, RTsafe’s patient-specific quality assurance process that comprises an anatomically faithful model of each patient’s head aligned to dosimetric evaluation services. The technology enables medical physicists and clinicians to verify the entire treatment process before the actual patient is subjected to radiotherapy.
Commenting on the announcement, Evangelos Pappas, Founder and Chief Scientific Officer at RTsafe said: “We are delighted that IVO, Spain’s internationally renowned centre of excellence in cancer treatment, has embraced the concept of assuring patient safety and treatment efficiency through human-like simulation of the stereotactic radiosurgery process.”
The simulation was carried out ahead of IVO’s first patient treatment using the new TrueBeam linear accelerator from Varian Medical Systems, a Siemens Healthineers company, that integrates radiotherapy and image-guided radiosurgery on the same platform. The machine was acquired as part of the ongoing efforts by IVO’s Radiation Oncology Service to increase patient safety and treatment quality.
A case study published by medical technology distribution company, Aplicaciones Tecnológicas de la Física, points out that due to the complexity of administering SRS plans, periodic quality control protocols and pre-treatment dose verification procedures based on the actual patient anatomy are advisable and could improve treatment efficiency.
The PseudoPatient treatment verification process begins with the construction of a 3D-printed phantom based on the individual patient’s CT scan, accurately reproducing the bone anatomy. The phantom is then filled with a special polymer gel developed by RTsafe that acts as both a soft tissue equivalent material and a 3D dosimeter. The end-to-end radiosurgery procedure is then performed just as it would be on the real patient. The irradiated phantom is then MRI scanned and changes in gel’s magnetic properties reveal the treated areas. RTsafe then provides a comprehensive quantitative and qualitative report in order to assist the clinical team in either verifying the treatment plan or making adjustments to it.
Conventional patient-specific quality control methods involve dose measurements on a standard-shaped phantom equipped with several detectors with the aim of verifying the treatment plan. However, dose treatment verification based on the actual patient anatomy may be critical in minimising unwanted exposure to radiation. RTsafe’s development of PseudoPatient seeks to solve the limitations presented by generic phantoms thereby achieving more rigorous quality control in stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) treatments.
Evangelos Pappas added: “Brain metastases can occur in more than 30% of all cancer patients and, while SRS is a good treatment option for many patients, its complexity means that accurate pre-treatment dose verification could make a difference to treatment outcomes should an adjustment to dosage or targeting be indicated by the simulation process. The approach improves the confidence of both medical professionals and patients in this exacting treatment method.”
Read the full case study here: http://bit.ly/3i1Lxp7.

 August 09, 2024
August 09, 2024