August 31, 2015 — Researchers using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) have found that even first-episode psychotic patients process information differently from a control group. To ensure both groups experienced the same brain stimuli, the measurements were taken while the subjects watched a movie, Tim Burton's Alice in Wonderland. The work is being presented at the 28th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology (ECNP) conference in Amsterdam.
High-precision fMRI is often used in neuroscience to locate brain activity in response to stimuli. With psychotic patients, these experiments often look at chronically ill patients, and so the differences in brain activity shown in the scans would be more obvious than in most of real life. However, early psychosis is more difficult to detect: the patterns in the brain are not as 'hard wired' so the differences are more subtle when compared to control groups.
Given the subtle differences, researchers are also faced with the problem of trying to ensure the patients and controls receive the same stimuli while undergoing measurement, so that the brains of the patients and the controls are concentrating on the same things while being scanned. Ideally, these stimuli should be involving and information-rich, like in a real-life situation.
Now a group of Finnish researchers have come up with a creative solution: Patients and controls were scanned while watching the movie Alice in Wonderland, which guaranteed that they were receiving the same information-rich stimulus.
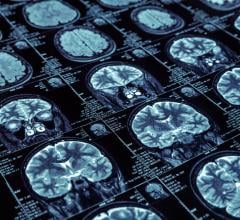
Using a 3-Tesla MRI device, they scanned the brains of 46 first-episode psychotic patients (meaning that they had only had one psychotic event) and 32 healthy controls, while watching the movie. The researchers found that significant differences could be seen in the precuneus region of the brain, which is an area associated with memory, visuospatial awareness, self-awareness and aspects of consciousness.
Lead researcher Eva Rikandi said: 'In this work, we attempted to determine whether a person is a first-episode psychosis patient or a healthy control subject just by looking at their brain activity recorded during movie viewing. We found, that by monitoring activity in a region known as the precuneus, we were able to distinguish patients from control subjects especially well. This would mean that the precuneus, a central hub for the integration of self- and episodic-memory-related information, plays an important role in this kind of information processing of psychotic patients.”
She continued: “We were able to achieve almost 80 percent classification accuracy using these methods. This is the first study which directly associates the beginnings of psychosis with the precuneus, so it is now important that much more research is done in this area'. The researchers hope that this approach can feed into earlier screening and better diagnosis of at-risk populations.”
ECNP President-Elect Prof. Celso Arango (Madrid) said, "The interesting question here is how patients with psychosis, even in their first episode, process information in a different way. Specifically how a movie such as Alice in Wonderland elicits the participation of different brain areas, and how that relates to the history of the person watching. What we would like to know is if patients with psychosis might see this as more or less relevant to their own life than would healthy controls. This movie is about a fantasy world, would it be different with other types of movie?"
For more information: www.ecnp-congress.eu


 July 25, 2024
July 25, 2024