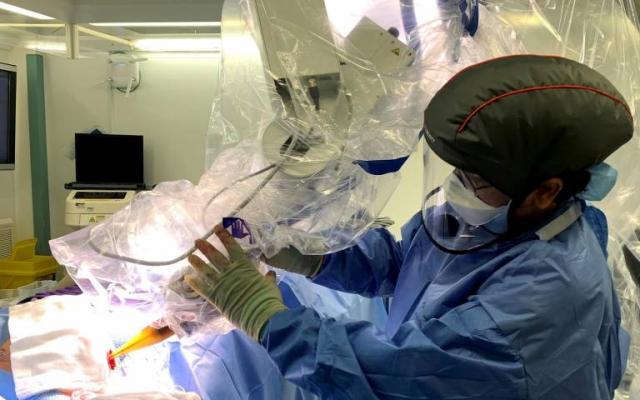
Prof. Jayant Vaidya, lead author of the study, University College London surgery and interventional science, performs a TARGI-IORT procedure. A small ball-shaped device placed inside the breast, directly where the cancer had been. The single-dose treatment lasts for around 20-30 minutes and replaces the need for extra hospital visits in eight out of ten cases.
June 2, 2021 — A breast cancer therapy that requires just one shot of radiotherapy is as effective as traditional radiotherapy, and avoids potential damage to nearby organs, according to a paper by UCL experts.
The results, published in the British Journal of Cancer, mean that eight out of ten patients who receive the treatment, TARGIT-IORT, will not need a long course of post-operative external beam radiotherapy (EBRT).[1] These results strengthen and expand previously published outcomes.
Patients who received the treatment are less likely to go on to experience fatal cardiovascular disease such as heart attacks, lung problems or other cancers. As well as avoiding scattered radiation from EBRT that can damage nearby vital organs, delivering TARGIT-IORT during the lumpectomy procedure seems to lower the likelihood of death if patients do go on to develop cardiovascular disease, protecting in a drug-like manner. This was the case even when EBRT was also given post-operatively, and is thought to be because the treatment changes the microenvironment in the lumpectomy wound.
The researchers say that delivering radiation immediately to the site where the tumour was can reduce the adverse effects of surgical trauma make the site less conducive for cancer growth and could have an 'abscopal' (distant) effect. This is where a treatment such as radiotherapy has a positive effect on tissue away from the operation site, which is increasingly recognised as a beneficial immunological action.
Previous studies have shown that the treatment has fewer radiation-related side effects compared with conventional whole breast radiotherapy, with less pain, a superior cosmetic outcome with fewer changes to the breast as a whole and a better quality of life.
"With TARGIT-IORT, women can have their surgery and radiation treatment for breast cancer at the same time. This reduces the amount of time spent in hospital and enables women to recover more quickly, meaning they can get back to their lives more quickly," explained lead author Professor Jayant Vaidya, UCL surgery and interventional science.
TARGIT-IORT is delivered immediately after tumour removal (lumpectomy), and under the same anaesthetic, via a small ball-shaped device placed inside the breast, directly where the cancer had been. The single-dose treatment lasts for around 20-30 minutes and replaces the need for extra hospital visits in eight out of ten cases.
Further tumour subgroup analysis also found that there was a significant overall survival benefit with TARGIT-IORT in patients with grade 1 or 2 cancer.
"These new results make it clear that the TARGIT-IORT is effective in all tumour subgroups of invasive duct cancer, the most common type of breast cancer," Professor Vaidya added. "Our new online tool can help clinicians make a decision about additional radiotherapy (recommended in a small proportion of cases) for each individual patient. The finding that fewer deaths are from the avoidance of scattered radiation and the possible abscopal effect of TARGI-IORT is important and should fuel further research, opening doors to new treatments."
For the clinical trial, which started in March 2000, 2,298 women aged 45 or over with invasive breast cancer and a tumour up to 3.5 cm in diameter were randomly assigned to receive either TARGIT-IORT during lumpectomy or post-operative EBRT.
The trial was designed and run from UCL, involved 32 hospitals and medical centres in ten countries: the U.K., France, Germany, Italy, Norway, Poland, Switzerland, the U.S., Canada and Australia.
These results are the highest level of evidence proving not only the effectiveness of TARGIT-IORT but confirming that it avoids deaths from other causes, said Professor Michael Baum, UCL Surgery and Interventional Science. "The new data is biologically very interesting and the new tools will make its application in routine clinical practice much easier. I am pleased that it will benefit thousands of breast cancer patients around the world."
"With TARGIT-IORT, the majority of patients presenting with early localised breast cancer will never need any further radiotherapy," said Professor Jeffrey S. Tobias, professor of clinical oncology, UCL and UCLH. "They will avoid all the side effects of whole breast radiotherapy. The chance of remaining free of local recurrence (in the breast itself) is the same as with traditional treatment, but our new analysis shows that even if they do get a local relapse, it will not detract from an excellent prognosis — as good as not having a relapse — a rather different state of affairs from the more serious outlook if this were to happen after EBRT."
To date, 45,000 patients in 260 centres in 38 countries have received TARGIT-IORT. The clinicians hope that following the latest results, more patients can be offered the treatment both in the U.K. and around the world instead of EBRT.
For more information: www.
Related TARGIT-IORT Content:
Single Dose Radiotherapy as Good as Conventional Therapy for Most With Early Breast Cancer
Reference:

 August 09, 2024
August 09, 2024