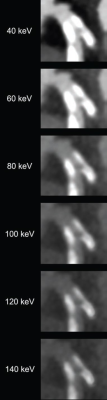
82-year-old man with calcified stenosis in left main artery who underwent coronary CTA by PCD CT. Curved multiplanar reformatted images at varying virtual monoenergetic imaging (VMI) levels (40-140 keV) show stenosis at each level. Percent diameter stenosis (PDS) decreased from 92.5% at 40 keV to 53.1% at 140 keV. Extent of calcium blooming artifacts decreased from 100.0% at 40 keV to 72.3% at 140 keV.
January 11, 2024 — According to the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), photon-counting detector (PCD) CT with virtual monoenergetic imaging (VMI) reconstruction can help overcome present limitations in stenosis quantification on coronary CTA.
“When performing coronary CTA by PCD CT, the selection of VMI level influences stenosis assessment in calcified and mixed plaque, thereby potentially impacting clinical decision-making,” wrote corresponding author Tilman Emrich, MD, from the department of diagnostic and interventional radiology at Germany’s University Medical Center in Mainz.
In this AJR accepted manuscript, a phantom containing two custom-made vessels (25% and 50% stenoses) underwent PCD CT acquisitions without and with simulated cardiac motion. A retrospective analysis was performed of 33 patients (7 female, 26 male; mean age, 71 years; 64 coronary artery stenoses) who underwent coronary CTA by PCD CT followed by invasive coronary angiography (ICA). Scans were reconstructed at nine VMI levels (40–140 keV). Percentage diameter stenosis was measured, and bias was determined from the ground-truth stenosis percentage in the phantom and ICA-derived quantitative coronary angiography measurements in patients. Extent of blooming artifacts was measured in the phantom and in calcified and mixed plaques in patients.
Ultimately, for coronary CTA performed by PCD CT, stenosis percentage and calcium blooming artifacts decreased with increasing VMI level in calcified and mixed plaque. Stenosis measurement exhibited lowest bias, using invasive angiography as reference, at 100, 140, and 40 keV for calcified, mixed, and non-calcified plaque, respectively.
“To our knowledge,” Emrich et al. added, “this study is the first in vivo study to investigate the influence of different VMI levels on stenosis quantification of PCD CT in comparison with ICA as the reference standard.”
For more information: www.arrs.org


 August 09, 2024
August 09, 2024