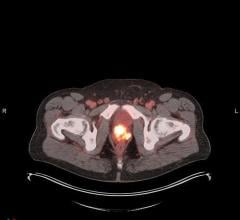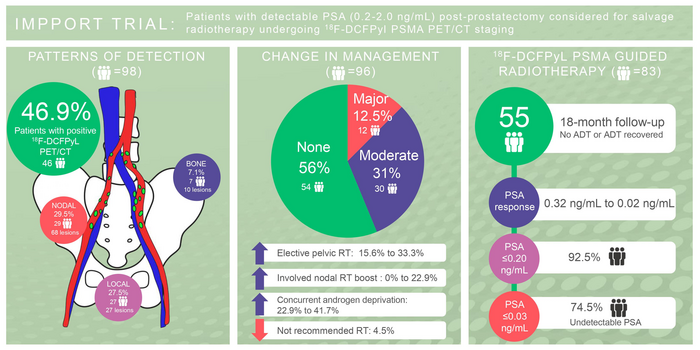
Patients with detectable PSA (0.2-2.0 ng/mL) post-prostatectomy considered for salvage radiotherapy undergoing 18F-DCFPyl PSMA PET/CT staging. Image created by M.Ng et al, GenesisCare, Melbourne, Australia.
September 8, 2022 — In prostate cancer patients experiencing recurrence following a radical prostatectomy, imaging with 18F-DCFPyL PSMA PET/CT has been shown to considerably improve detection of active disease as compared to imaging with CT alone. As reported in the September issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, detailed PET/CT scans resulted in a change in treatment plans for nearly 50 percent of patients.
Prostate specific antigen (PSA) recurrence—defined as a PSA level higher than 0.2ng/mL—occurs in 20 to 50 percent of all radical prostatectomy cases. In more than half of these patients, subsequent treatment with salvage radiotherapy (most commonly to the prostate bed) results in five-year biochemical control.
“For those patients who are experiencing a recurrence, it’s important to determine exactly where the cancer has spread so that it can be treated effectively with salvage radiotherapy,” said Michael Ng, MBBS (Hons), FRANZCR, radiation oncologist at GenesisCare St Vincent’s Hospital in Melbourne, Australia. “We know that prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) radiotracers have increased sensitivity in the detection of prostate cancer compared to conventional imaging. In this study we assessed the management impact of a novel PSMA tracer, 18F-DCFPyL PSMA PET/CT, in patients being considered for salvage radiotherapy.”
This study included 100 patients presenting with a detectable PSA following radical prostatectomy. Following patient registration and prior to any imaging, radiation oncologists outlined each patient’s “original intent” treatment plan on a questionnaire. All patients then underwent diagnostic CT and 18F-DCFPyL PSMA PET/CT. The CT results were released first, and a second “post-CT intent” questionnaire was completed. Next, the 18F-DCFPyL PSMA PET/CT results were released and a final “post-PSMA intent” questionnaire was completed. Change in management was graded based on impact and defined as major, minor, or no change demonstrated.
18F-DCFPyL PSMA PET/CT detected disease in 46.9 percent of patients compared to 15.5 percent on diagnostic CT. Major changes in the treatment plan were more likely to occur after PSMA imaging (12.5 percent) than after CT imaging (3.2 percent), and moderate changes were noted in 31.3 percent of patients after PSMA imaging versus 13.7 percent after CT imaging. The most common changes were recommendations for additional treatment, such as elective pelvic radiation, nodal boost, or concurrent androgen deprivation therapy.
Follow-up data were available at 18 months for 59 of the individuals in the study. At that timepoint, 92.5 percent had a PSA of below 0.20ng/mL and 74.5 percent had an undetectable (less than 0.03ng/mL) PSA.
“This research is novel as utilization of PSMA PET/CT allows earlier detection of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy. The prospective study carefully collected changes in decision making and tracked the impact on patient management with outcome data available in patients who underwent radiotherapy,” noted Dr. Ng. “The group of patients studied—all post-surgery without other confounding treatments (no prior radiotherapy and no prior drug therapy) with a low and focused PSA range between 0.2-2.0ng/mL— reflects a common management problem. The study’s results are timely and applicable for patients experiencing their first recurrence after prostate surgery.”
For more information: www.snmmi.org
Related prostate cancer content:
SNMMI Applauds FDA Approval of New Metastatic Prostate Cancer Treatment
PSMA PET Validates EAU Classification System to Determine Risk of Prostate Cancer Recurrence
VIDEO: MRI-Linac and PSMA PET Imaging Technologies Aids Therapy at GenesisCare
FDA Approves First Commercially Available PSMA PET Imaging Agent for Prostate Cancer
PSMA-Targeted Radiotracer Pinpoints Metastatic Prostate Cancer Across Anatomic Regions
Metastatic Prostate Cancer on the Rise Since Decrease in Cancer Screenings
Rational Surgical Solutions’ mCRPC Master Now Offered as Free Download


 April 21, 2025
April 21, 2025