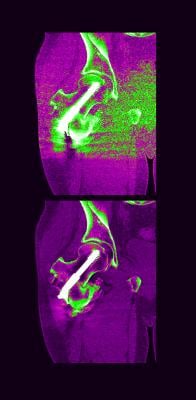
March 12, 2014 — The Hospital for Special Surgery in collaboration with GE Healthcare developed an MRI that can show a detailed image following hip fracture repair. It does so without the distortion caused by metal surgical screws that are problematic in standard MRIs.
Each year, more than 340,000 people suffer a broken hip in the United States. The femoral neck is the most common site of fracture, accounting for 45 to 53 percent of cases. People with this type of injury are at high risk of complications because the blood supply to the fractured portion of the bone is often disrupted. The concern is that the decreased blood supply will lead to osteonecrosis.
Researchers at Hospital for Special Surgery developed a specially sequenced, contrast-enhanced MRI to identify potential problems so doctors can intervene early and prevent further damage to the joint.
"This new MRI greatly improves the visualization of bone and soft tissue when there is metal in a joint, such as the screws used to repair a hip fracture," said Hollis G. Potter, M.D., chairman of the department of radiology and imaging at HSS.
A study titled "Femoral Head Osteonecrosis Following Anatomic Stable Fixation of Femoral Neck Fractures: An in-vivo MRI Study" was presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) in New Orleans, March 11.
Despite advances in surgical hardware and techniques, femoral neck fractures remain a significant clinical challenge. The primary complications arising from femoral neck fractures are non-union and osteonecrosis when the blood supply to the bone is disrupted.
With respect to femoral neck hip fractures, this is the first MRI that can "see through" surgical screws to detect early signs of osteonecrosis, so that interventions can be initiated before there is further damage, such as collapse of the bone or osteoarthritis.
In the study, patients had an MRI known as a "multi-acquisition variable-resonance image combination," or MAVRIC MRI, three months and 12 months after surgery. "The MAVRIC MRI provided us with information that could not be ascertained from x-rays or a standard MRI," Potter said. "A special 3-D fast spin echo technique minimized distortion caused by metal screws used to repair the fracture, facilitating assessment of the hip joint and any potential problems concerning osteonecrosis or non-union."
MRI revealed decreased blood flow to the injured area and osteonecrosis in 80 percent of patients in the superomedial quadrant of the femoral head. However, despite these findings, patients demonstrated excellent radiographic and functional outcomes. Researchers attributed this to a surgical technique that entailed stabilizing the broken bones with screws and restoring the fracture to the correct alignment and normal anatomical position.
For more information: www.hss.edu
