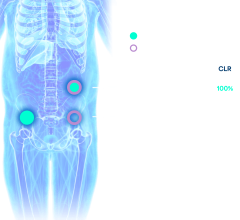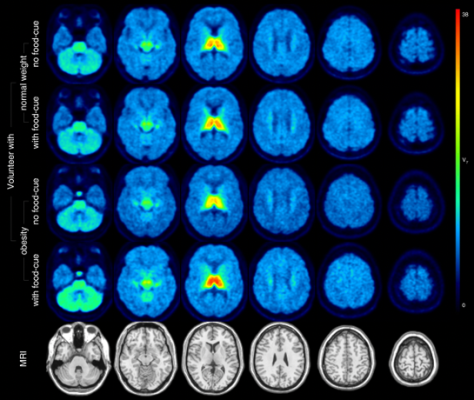
Figure 1. Distribution volumes of α4β2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain of normal-weight volunteers and volunteers with obesity.
June 28, 2023 — Molecular imaging with 18F-flubatine PET/MRI has shown that neuroreceptors in the brains of individuals with obesity respond differently to food cues than those in normal-weight individuals, making the neuroreceptors a prime target for obesity treatments and therapy. This research, presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2023 Annual Meeting, contributes to the understanding of the fundamental mechanisms underlying obesity and offers valuable insights into potential medical interventions.
Worldwide, more than one billion people are obese. The global obesity epidemic poses a major challenge for health care systems worldwide, and the search for interventions to achieve sustainable weight loss is a high priority. By investigating biological and behavioral mechanisms in individuals with obesity, scientists are seeking to identify potential pathways for treatments and interventions.
“The brain’s cholinergic system is a unique area of interest when it comes to studying obesity,” said Swen Hesse, MD, clinical scientist and professor in the Department of Nuclear Medicine at the University of Leipzig in Leipzig, Germany. “Cholinergic changes in the brain’s reward and attentional networks seem to play an important role in how people decide what foods are most desirable, or salient. In our study, we aimed to measure changes in α4β2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors found in the cholinergic system in response to high-caloric food cues.”
In the study, 15 individuals with obesity and 16 normal-weight controls underwent PET/MRI with 18F-flubatine twice on separate days, once while in a resting state and once while viewing food pictures. Total distribution volume of 18F-flubatine was estimated, and a visual analog scale was used to assess states of hunger/satiety, appetite, disinhibition, craving and taste. Eating behavior was also measured using the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire (TFEQ).
In the resting state, no significant difference in total distribution volume of 18F-flubatine was noted between the participants with obesity and normal-weight controls. While viewing photos of food, however, the total distribution volume of 18F-flubatine was higher in the obese compared with normal-weight controls in the thalamus of the brain, particularly in those with a higher TFEQ score.
For normal-weight controls there was a stronger connectivity to the dorsal attention network of the brain when viewing food cues, whereas for participants with obesity, a stronger connectivity was found with the salience network. Finally, analyses of the total volume distribution and different behavioral measures showed significant correlation between total volume distribution in the hypothalamus and measure for satiety in normal-weight controls. In participants with obesity there was a significant correlation with measures of disinhibition and the nucleus accumbens.
“We anticipate that the results of our study will pave the way for novel drug treatments and behavioral interventions to effectively combat obesity worldwide,” noted, Osama Sabri, MD, PhD, professor, director, and chairman of the Department of Nuclear Medicine at the University of Leipzig. “In addition, the imaging technology utilized in this study holds promise for identifying biomarkers that can aid in patient stratification and facilitate personalized medicine approaches in the near future.”
For more information: www.snmmi.org
Find more SNMMI23 coverage here

 July 30, 2024
July 30, 2024