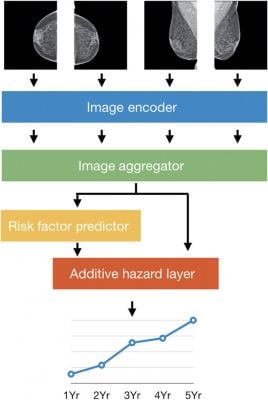
The four standard views of an individual mammogram were fed into Mirai. The image encoder mapped each view to a vector, and the image aggregator combined the four view vectors into a single vector for the mammogram. In this work, we used a single shared ResNet-18 as an image encoder, and a transformer as our image aggregator. The risk factor predictor module predicted all the risk factors used in the Tyrer-Cuzick model, including age, detailed family history, and hormonal factors, from the mammogram vector. The additive hazard layer combined information from both the image aggregator and risk factors (predicted or given) to predict coherent risk assessments across 5 years (Yr).
January 28, 2021 — A new machine learning algorithm based on mammograms can estimate the risk of breast cancer in women more accurately than current risk models, according to a study from Adam Yala and colleagues. The algorithm, which was tested with datasets from three large hospitals located worldwide, could help clinicians design guidelines for breast cancer screening that meet the need for early detection while reducing false-positives, test costs, and other issues associated with overscreening. Mammograms are the most common method to screen for breast cancer, as more than 39 million procedures are performed in the U.S. annually. However, their widespread adoption has not gone without controversy. Critics charge that aggressive screening results in untenable medical costs, higher anxiety in patients, and a substantial rate of false positives. On the other hand, supporters of frequent testing argue it is necessary to detect tumors as early as possible, and the disagreement has led to inconsistent guidelines for when screening should start and how frequent it should be. Yala et al. theorized that improving the accuracy of the risk models that inform guidelines could lead to better recommendations. They designed and trained a new model named Mirai, which integrates data from mammograms to produce consistent breast cancer risk assessments at multiple time points, such as within 1 year or 5 years. When independently tested with data from 106,615 patients from three hospitals, located in the U.S., Sweden, and Taiwan, Mirai identified 41.5% of patients who would develop cancer within 5 years. In contrast, current approaches such as the Tyrer-Cuzick and Hybrid Deep Learning models only identified 22.9% and 36.1% of patients, respectively. Mirai was also effective across various races and ethnicities, supporting its potential to inform screening guidelines for large and diverse populations.
For more information: www.aaas.org


 March 21, 2025
March 21, 2025