March 19, 2021 — Many women suffering significant postpartum bleeding continue to receive hysterectomies, rather than uterine artery embolization (UAE), despite evidence that UAE results in reduced hospital stays and costs, and offers an opportunity to preserve fertility, according to new research to be presented at the Society of Interventional Radiology Annual Scientific Meeting.
“Giving birth has become increasingly dangerous for women in the U.S., and postpartum hemorrhage is a leading cause of the loss of life related to childbirth,” said Janice M. Newsome, M.D., FSIR, associate professor, Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences at Emory University School of Medicine and a lead author of the study. “All patients should have consistent access to a treatment that is safer, has an easier recovery and could preserve their ability to continue to have children.”
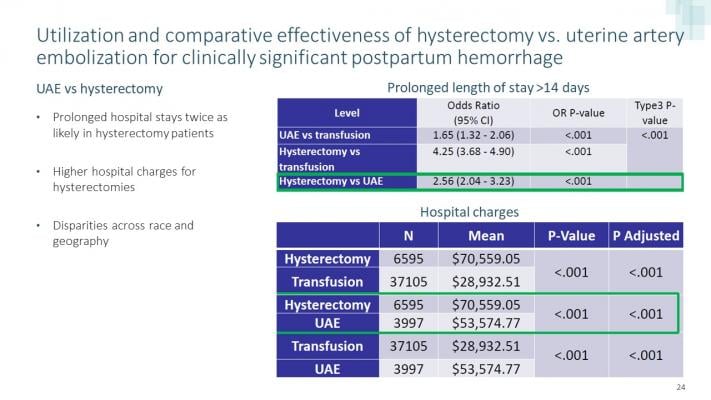
In a review of nearly 10 million hospital births between 2005 and 2017, researchers found the most common intervention was transfusion, but removal of the uterus through hysterectomy was used 60% more often to manage bleeding than UAE, a minimally invasive procedure that uses real-time imaging to release tiny particles into uterine arteries to control the bleeding. Hysterectomy was twice as common as embolization in Hispanic patients, and also more common in rural and nonteaching urban hospitals, in the South and among Medicaid and self-paying patients.
Prolonged hospital stays of more than 14 days were twice as likely in patients who had hysterectomies and the procedure resulted in $18,000 higher hospital charges.
“Postpartum hemorrhage can occur quickly, and effective treatment options should be readily available to every woman having a child in the United States,” said Newsome. “For hospitals that have IR services available, this can be accomplished by creating a concrete care plan for new mothers who are at higher risk of dangerous bleeding during childbirth.”
Newsome envisions creating postpartum hemorrhage response teams, similar to other trauma teams, that would train together and develop response protocols, so that they are better able to identify risk factors of postpartum hemorrhage and ensure the right staff are on hand for delivery to respond quickly and save mothers’ lives before it gets to the point of needing radical surgery.
Researchers used the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project Nationwide Inpatient Sample database, which tracks every hospital admission in the United States, and examined the results of significant postpartum bleeding, which occurred in 3.1 percent of live births.
For more information: www.sirmeeting.org


 July 28, 2025
July 28, 2025