July 23, 2012 — GE Healthcare announced the final results from a Phase III study of the investigational PET (positron emission tomography) amyloid imaging agent, F-18 flutemetamol, in terminally ill patients who had agreed to undergo postmortem brain autopsy. The data showed strong concordance (sensitivity and specificity) between flutemetamol PET images and beta amyloid brain histopathology. These data confirm the potential of flutemetamol as an imaging agent to detect beta amyloid plaque, a pathology associated with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), in living patients.
The data were presented at the Alzheimer's Association International Conference 2012 (AAIC 2012) in Vancouver, British Columbia, and support an application for regulatory approval of flutemetamol, which is intended to be filed later this year. Flutemetamol is a GE Healthcare PET imaging agent in development for the detection of beta amyloid deposits in the brain.
“Currently, definite AD diagnosis requires postmortem examination of the brain for pathology such as neuritic beta amyloid plaques,” said Milos Ikonomovic, M.D., associate professor of neurology at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center and presenter of the study. “Because the ability to detect brain amyloid deposits in vivo may allow physicians to make a more accurate clinical diagnosis and potentially could enhance patient management, we were pleased to see that flutemetamol PET images accurately and consistently reflected fibrillar beta amyloid levels as detected later using postmortem histopathology analyses.”
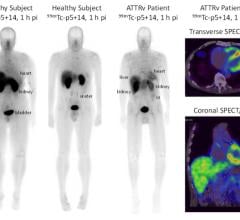
The study presented at AAIC 2012 examined the autopsied brains of 68 subjects who had received flutemetamol imaging in life to detect the presence of brain beta amyloid pathology. The images were then evaluated visually by independent trained readers, and the flutemetamol retention in the brain was quantified using a standardized uptake value ratio (SUVR). The brains of subjects who subsequently died were evaluated histopathologically and compared to interpretations of flutemetamol PET scans.
Flutemetamol showed the ability to detect beta amyloid with a majority read sensitivity of 86 percent and specificity of 92 percent. Sensitivity is the percentage of amyloid-positive brains that are correctly identified by flutemetamol image readers as abnormal, corresponding to positive amyloid pathology. Comparison within and between image readers documented strong consistency of interpretation.
The accumulation of beta amyloid in the brain is believed to play a role in the degeneration of neurons in AD and is one of several pathological characteristics implicated in its development. Currently, AD is confirmed by histopathological identification of core features, including beta amyloid plaques, in postmortem brain samples. Targeted amyloid imaging agents are being studied to determine their ability to help physicians detect amyloid deposition in living humans.
“The detection of beta amyloid plaque in vivo may enable physicians to clinically diagnose AD earlier, potentially improving patient care,” said Jonathan Allis, general panager, PET, GE Healthcare Medical Diagnostics. “Flutemetamol imaging has the potential to be part of a larger diagnostic workup that may help doctors rule out AD by reliably showing the absence of amyloid deposits in patients with unexplained loss of cognitive function. We are pleased to report that flutemetamol acted as anticipated in this study and look forward to filing with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).”
For more information: www.gehealthcare.com

 July 30, 2024
July 30, 2024