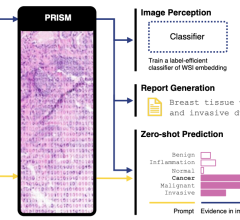
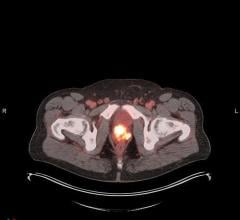
March 4, 2014 — Advanced Accelerator Applications (AAA), a growing international player in molecular nuclear medicine, announced they have received orphan drug designation status for their radiopharmaceutical, Gallium-68 Dotatate. The orphan drug designation has been granted by both the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for use of Gallium-68 Dotatate as a diagnostic agent for the management of gastro-entero-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs). The designation should foster rapid development of the agent for the benefit of GEP-NET patients in the United States and Europe.
Gallium-68 Dotatate is a radiopharmaceutical used in PET/CT (positron emission tomography/computed tomography) imaging of GEP-NETs. The product will be prepared using AAA’s patented kit, which is reconstituted in hospital radiopharmacies without the use of a radiochemistry module, thus making the product available to all hospitals, even those who do not have a fully equipped GMP production radiopharmacy unit.
Existing data show that the Gallium-68-labeled PET radiopharmaceutical should represent a major improvement compared to the current standard. Available data indicates that Gallium-68 Dotatate not only has greater sensitivity and specificity for tumor detection than the current standard, but it is also expected to significantly reduce radiation doses received by patients.
Stefano Buono, CEO of AAA, commented, “GEP-NETs constitute a life-threatening disease and effective patient management requires accurate diagnostic tools. The orphan drug designation of AAA’s Gallium-68 Dotatate will accelerate the development of this agent and hopefully allow it to be available to patients in the next few years. ”
“Receiving orphan drug designation for Gallium-68 Dotatate is an important step in the overall approval process. It reinforces our position and interest in NETs, both on the diagnostic and treatment front. Strong literature evidence already exists about the efficacy of Gallium-68 Dotatate, which we believe reduces our development risks for this product,” added Gérard Ber, AAA’s chief operating officer.
The EMA's orphan medicinal product designation is designed to promote the development of drugs that may provide significant benefit to patients suffering from rare, life-threatening diseases. In addition to ten years of market exclusivity, the orphan drug designation also provides special incentives for sponsors including eligibility for protocol assistance and possible exemptions or reductions in certain regulatory fees during development or at the time of application for marketing approval.
Similarly, FDA orphan drug designation is intended to encourage companies to develop therapies for the treatment of diseases that affect fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States. This designation could provide AAA with seven years of marketing exclusivity for AAA’s Gallium-68 Dotatate as a diagnostic agent for the management of GEP-NETs if it receives first approval by the FDA. Prior to FDA approval, orphan designation by the FDA provides the opportunity to obtain grant funding to help finance costs of clinical trial expenses, tax credits for clinical research expenses and potential waiver of the FDA's application user fees.
For more information: www.adacap.com

 July 30, 2024
July 30, 2024