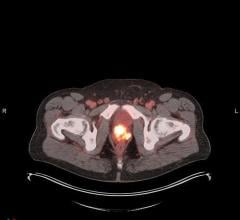
Janaury 10, 2022 — The Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) and Office of Environmental Management (DOE-EM) have signed the first contracts as part of the Department’s Uranium Lease and Take-back Program with SHINE Technologies LLC. This is a milestone in the Department’s effort to increase domestic production of molybdenum-99 (Mo-99), a crucial medical isotope used in over 40,000 medical procedures in the United States each day, without the use of highly enriched uranium (HEU).
NNSA’s lease contract will provide SHINE with the low-enriched uranium necessary to produce Mo-99 while DOE-EM’s contract details requirements surrounding the return of any resulting radioactive waste unable to be disposed of commercially once Mo-99 production is complete.
“Signing these contracts with SHINE is a crucial step toward medical isotope autonomy for the United States,” said Corey Hinderstein, NNSA Deputy Administrator for Defense Nuclear Nonproliferation. “Once SHINE begins production, our country will be that much closer to creating a reliable and sufficient supply of these life-saving materials right here at home, while also increasing nuclear security by reducing the use of highly enriched uranium.”
The American Medical Isotopes Production Act of 2012 directed DOE/NNSA to establish a program to make uranium available to medical isotope producers in the United States. Although the Act also requires DOE to establish take-back contracts for spent nuclear fuel and radioactive waste resulting from medical isotope production without a disposal path, there is no spent fuel involved in these contracts.
NNSA’s Mo-99 program works to ensure a stable, domestic supply of this critical isotope while also reducing the use of HEU in Mo-99 production. Reducing the use of HEU increases nuclear security because HEU could be used in creating a nuclear or radiological weapon.
SHINE Technologies, LLC, of Janesville, Wisconsin, is one of NNSA’s cooperative agreement partners. In October 2021, NNSA awarded SHINE $35 million to support their efforts to produce Mo-99 commercially by the end of 2023.
To establish a reliable domestic Mo-99 production base in the United States, NNSA has also provided financial assistance to potential medical isotope producers. NNSA has implemented this by competitively awarding cost-shared cooperative agreements to commercial entities as well as providing funds to DOE’s National Laboratories to support development of non-HEU Mo-99 production technologies.
For more information: www.energy.gov/nnsa/national-nuclear-security-administration
Related Isotope Production News:
Shine Medical Approved to Build Domestic Molybdenum-99 Production Facility
BGN Technologies Introduces Novel Medical Imaging Radioisotope Production Method
Shine Medical Technologies Breaks Ground on U.S. Medical Isotope Production Facility


 November 12, 2025
November 12, 2025