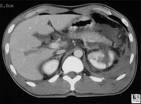
October 7, 2009 - Computed tomography (CT) is the modality of choice in the evaluation of blunt renal injury, according to a study published in the September 2009 issue of Radiolographics.
In the study, Imaging of Renal Trauma: A Comprehensive Review, intravenous urography is used primarily for gross assessment of renal function in hemodynamically unstable patients. Selective renal arteriography or venography can provide detailed information regarding vascular injury. Retrograde pyelography is valuable in assessing ureteral and renal pelvic integrity in suspected ureteropelvic junction injury. Ultrasonography is useful in detecting hemoperitoneum in patients with suspected intraperitoneal injury, but has limited value in evaluating those with suspected extraperitoneal injury. Occasionally, radionuclide renal scintigraphy or magnetic resonance imaging may prove helpful.
Renal injuries can be classified into four large categories based on imaging findings. Category I renal injuries include minor cortical contusion, subcapsular hematoma, minor laceration with limited perinephric hematoma, and small cortical infarct. Category II lesions include major renal lacerations extending to the medulla with or without involvement of the collecting system and segmental renal infarct. Category III lesions are catastrophic renal injuries and include multiple renal lacerations and vascular injury involving the renal pedicle. Category IV injuries are ureteropelvic junction injuries.
CT is particularly useful in evaluating traumatic injuries to kidneys with preexisting abnormalities and can help assess the extent of penetrating injuries in selected patients with limited posterior stab wounds. Integration of the imaging findings in renal injury with clinical information is critical in developing a treatment plan.
Reference: Kawashima, M.D., Akira, Sandler, M.D., Carl M., Corl, M.S., Frank M., West, M.D., O. Clark, Tamm, M.D., Eric P., Fishman, M.D., Elliot K., and Goldman, M.D., Stanford M., Imaging of Renal Trauma: A Comprehensive Review. Radiographics. September 2009. http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/21/3/557.abstract


 August 09, 2024
August 09, 2024