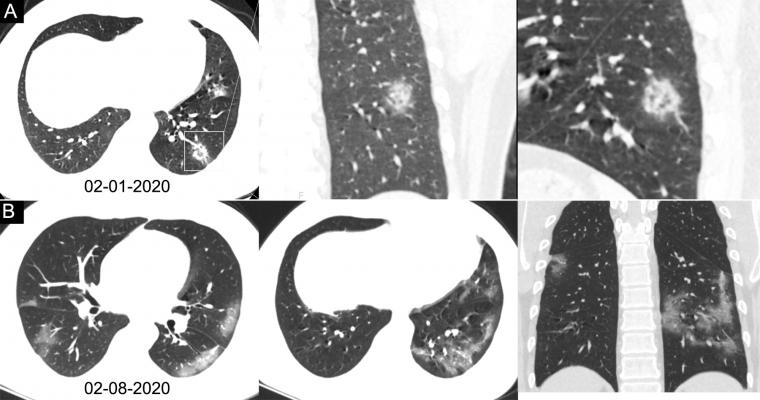
Chest CT images in a 34-year-old man with fever for 4 days. Positive result of reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction assay for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 using a swab sample was obtained on February 8, 2020. Dates of examination are shown on images. A, Chest CT scan with magnification of lesions in coronal and sagittal planes shows a nodule with reversed halo sign in left lower lobe (box) at the early stage of the pneumonia. B, Chest CT scans in different axial planes and coronal reconstruction show bilateral multifocal ground-glass opacities. The nodular opacity resolved.
November 29, 2020 — The Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) presented its ninth Alexander R. Margulis Award for Scientific Excellence to Liming Xia, M.D., Ph.D., for the Radiology article, “Correlation of Chest CT and RT-PCR Testing in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A Report of 1014 Cases,” published online in February 2020. The study found that chest CT outperformed lab testing in the diagnosis of COVID-19.
Named for Alexander R. Margulis, M.D., a distinguished investigator and inspiring visionary in the science of radiology, this annual award recognizes the best original scientific article published in RSNA’s peer-reviewed journal Radiology.
The Margulis Award Selection Committee chose the research by Dr. Xia and colleagues due to its critical impact on the diagnosis of COVID-19 early in the outbreak.
Xia, chief physician and chairman of the Department of Radiology at Tongji Hospital of Tongji Medical College in Wuhan, China, was among the first to study the role of chest CT in diagnosing a then unknown viral pneumonia that broke out in December 2019 in Wuhan.
“In a study of more than 1,000 patients, this outstanding research paper offered critical information to radiologists worldwide in the earliest days of the pandemic regarding the use of CT scanning,” said Radiology Editor, David A. Bluemke, M.D., Ph.D.
COVID-19 spread quickly throughout the world. With no therapeutic drugs or vaccines available to treat the novel virus, early diagnosis of COVID-19 was crucial for disease treatment and control.
“It was a difficult time,” Xia said. “We knew little about the disease, and the most urgent goal was to contain the spread of COVID as much as possible.”
While reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), or gene sequencing for respiratory or blood specimen, was the standard for detecting COVID-19, the method had demonstrated a high false negative rate and low sensitivity, possibly hindering quick diagnosis and timely treatment.
“At the time, RT-PCR testing was in short supply with delays of up to a week for results,” Bluemke said.
In response to the crisis, Dr. Xia and colleagues quickly launched an investigation of the diagnostic value and consistency of chest CT compared to RT-PCR in detecting COVID-19.
“It was a huge challenge since our entire staff was heavily overloaded, but it was also a valuable opportunity to do research with great clinical and societal significance,” Xia said.
The study included 1,014 patients from Tongji Hospital, the largest hospital in Wuhan. All patients underwent both chest CT and RT-PCR tests between January 6 and February 6, 2020.
With RT-PCR results as the reference standard, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of chest CT in indicating COVID-19 infection were 97% (580 of 601 patients), 25% (105 of 413 patients), and 68% (685 of 1014 patients), respectively. The positive predictive value and negative predictive value were 65% (580 of 888 patients) and 83% (105 of 126 patients), respectively. The results showed that chest CT was more effective than RT-PCR lab testing in detection of COVID-19.
“Our data and analysis suggest that chest CT should be considered for COVID-19 screening, comprehensive evaluation and follow-up, especially in epidemic areas with high pretest probability for disease,” the authors wrote.
As the COVID-19 outbreak reaches the one-year mark, Dr. Xia has new perspective on the research he and his colleagues conducted at the height of the pandemic.
“While COVID-19 research has become more extensive, thorough and comprehensive, I feel our Radiology study fits into this large body of research as a pioneering attempt to study COVID-19 with modern imaging techniques and to take advantage of the high sensitivity and fast speed of CT, which in our experience helped contain the epidemic early in the outbreak,” Xia said.
Bluemke said the timing of the research early in the pandemic was particularly valuable to a world in the midst of crisis.
“At that time in particular, clinicians needed to understand the use of imaging for COVID-19 pneumonia,” Bluemke said. “The results of Dr. Xia and co-authors still serve today as the fundamental basis for this understanding.”
Dr. Xia expressed gratitude for the award and recognized the contributions of his co-authors. Dr. Xia’s Radiology study has been downloaded more than 400,000 times and has been cited more than 770 times.
Photo Gallery — How COVID-19 Appears on Medical Imaging
For more information: www.rsna.org


 December 10, 2025
December 10, 2025 









