Greg Freiherr has reported on developments in radiology since 1983. He runs the consulting service, The Freiherr Group.
RSNA 2018 Wednesday — AI Continues To Dominate
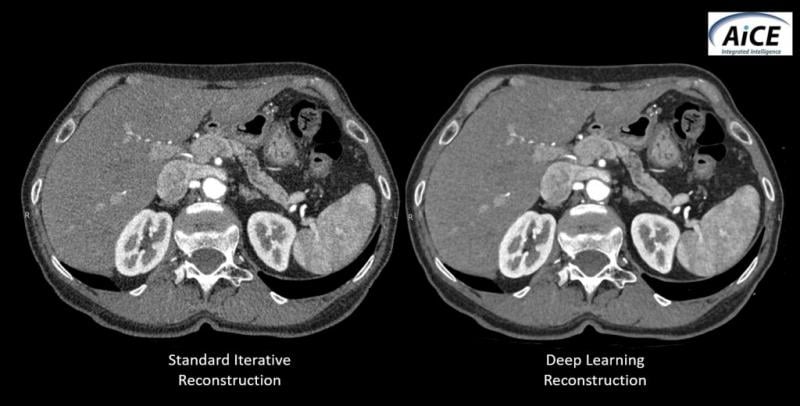
Comparison between CT images reconstructed using standard iterative reconstruction software and Canon’s new work-in-progress deep learning algorithm, called AiCE (Advanced intelligent Clear IQ Engine).
The practical application of artificial intelligence (AI) dominated the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), as the need for improved efficiency – a tenet of AI – was underscored.
Siemens Grooms AI Algorithms To Be Radiological “Companions”
 Two AI technologies, shown as works in progress at the Siemens booth (South Hall 4136), promise to simplify physicians’ professional lives. One, called AI-Rad Companion, is being framed as a platform for the development of intelligent software assistants capable of identifying organs and changes in tissue that may be early signs of disease. The other, called AI-Pathway Companion, is an AI-based clinical decision support system being developed to support physician decisions regarding diagnosis and therapy.
Two AI technologies, shown as works in progress at the Siemens booth (South Hall 4136), promise to simplify physicians’ professional lives. One, called AI-Rad Companion, is being framed as a platform for the development of intelligent software assistants capable of identifying organs and changes in tissue that may be early signs of disease. The other, called AI-Pathway Companion, is an AI-based clinical decision support system being developed to support physician decisions regarding diagnosis and therapy.
The first application coming out of the AI-Rad Companion platform is focused on chest computed tomography (CT), according to Siemens. The experimental AI-based application is being designed to differentiate among structures that appear in chest CTs; highlight certain structures; then mark and measure those that may be abnormal. Its objectives are to help radiologists interpret images faster and more accurately, and to reduce the time involved in documenting results. The ultimate goal is to increase productivity and quality, according to the company.
Preliminary testing has established that AI-Rad Companion Chest CT can identify lung lesions and calculate cardiovascular risk based on an analysis of coronary artery calcification on non-ECG-triggered CT images. The application may also help detect spine fractures due to osteoporosis.
AI-Pathway Companion is being groomed to provide physicians on patient management boards with the clinical status of the patient as indicated by different types of data and multi-modality images pulled together using AI algorithms. Additionally, the still experimental AI-Pathway Companion is intended to suggest to physicians possible steps to take in managing patients. Siemens expects the first clinical application to come from the AI-Pathway Companion to address prostate cancer.
Watch a VIDEO example of of this software for a prostate cancer patient.
Illumeo AI Fetches Prior Images Automatically
 Philips showed how AI is helping radiologists with faster workflow to improve care. Here is a VIDEO example the Philips Illumeo software showing a spine CT and how the radiologist can use the tool bar to gain one-click, immediate access to three prior CT studies that will open with the exact slate slice view and orientation as the current exam.
Philips showed how AI is helping radiologists with faster workflow to improve care. Here is a VIDEO example the Philips Illumeo software showing a spine CT and how the radiologist can use the tool bar to gain one-click, immediate access to three prior CT studies that will open with the exact slate slice view and orientation as the current exam.
Canon Uses AI to Advance CT Image Processing
At its booth (South Hall 1938) at RSNA 2018, Canon Medical is showcasing an artificial intelligence algorithm that “learns” to improve the resolution of CT images. The algorithm, which is pending FDA clearance, uses deep learning technology to tell the difference between noise and signal. It then uses what it has learned to suppress noise and enhance signal, according to the company.
Called Advanced intelligent Clear IQ Engine or AiCE (pronounced ACE), the still experimental algorithm learns to reconstruct CT images from the high quality images produced using model-based iterative reconstruction (MBIR). Although experience with the new algorithm is limited, AiCE has the potential to set a new standard for image reconstruction in CT, according to the company.
Caresteam Releases Results From Use of Workflow Orchestrator
Patient images can be read more efficiently when using Carestream Health’s Workflow Orchestrator, according to the company. Less than two months after Orchestrator went into service, interpreted cases increased by 15 percent at Renaissance Imaging Medical Associates (RIMA) of Northridge, California (one of the 10 largest private radiology groups in the United States), while 82 percent were assigned to a subspecialist highly qualified to read each specific case type, according to Carestream. (Workflow Orchestrator is designed to automatically assign studies to the most appropriate available radiologist while balancing caseloads to accelerate reading times.)
Study Of Imaging Efficiency Raises Doubts
Radiologists and radiographers may see their own efficiency as being better than it actually is. At RSNA 2018, Philips released the results of a study, commissioned by Philips and conducted by Suazio Consulting, in which 40 radiologists and radiographers were asked to rate themselves on their efficiency performing MRI scans. All but one said they were efficient or highly so — the average rating being 4 on a 5-point scale. Yet, the same respondents reported that 20 percent of their MR patients needed to be rescanned.
Often the cause for rescanning was patient motion. Almost half the respondents – 45 percent – reported not knowing that technologies are available to reduce the effects of patient motion and, consequently, reduce the number of rescans.
Improving Fetal Blood Flow Visualization
 The new Fetal HQ heart and vascular software from GE Healthcare being shown at RSNA may offer a big advancement for fetal ultrasound. The software, for the Voluson E10, helps evaluate the fetal heart shape, size and contractibility. A feature called Radiant Flow shows the blood flow in a 3-D view. It can also help show slow-flow blood, such as neuro-vascular circulation. Watch a VIDEO example of this technology.
The new Fetal HQ heart and vascular software from GE Healthcare being shown at RSNA may offer a big advancement for fetal ultrasound. The software, for the Voluson E10, helps evaluate the fetal heart shape, size and contractibility. A feature called Radiant Flow shows the blood flow in a 3-D view. It can also help show slow-flow blood, such as neuro-vascular circulation. Watch a VIDEO example of this technology.
Related RSNA 2018 Coverage:
RSNA 2018 Tuesday — Real Meets Virtual and AI
RSNA 2018 Sunday – Improving, Not Replacing
RSNA 2018 Monday — AI and Enterprise Imaging Gain Traction
VIDEO: RSNA President Says Artificial Intelligence is Hottest Tech Advancement in Radiology.
PODCAST Hear and Now: What You Need to Know About Enterprise Imaging


 August 29, 2024
August 29, 2024