September 24, 2014 — Mirada Medical software applied to state-of-the-art adaptive radiotherapy (ART) was the subject of an oral presentation at the annual conference of the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) earlier this month in San Francisco.
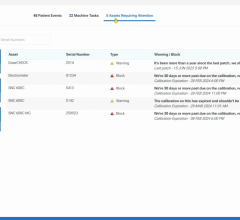
A critical yet hugely time-consuming step in ART is the monitoring of patients throughout the course of therapy to determine which need to be replanned. This need presents a significant barrier to adoption of ART methods in the clinic. The original research, presented by collaborators from the University Medical Center, Groningen, The Netherlands, examined the possibility of using advanced image registration methods to automate patient monitoring and to flag only those patients that might need further investigation. Such a method can create significant time-savings.
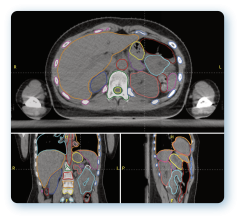
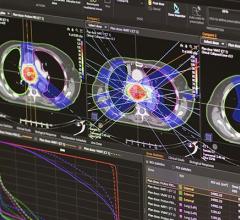
The study included 28 locally advanced head and neck cancer patients treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). For each patient, the planning target volumes and organs at risk were contoured on the planning computed tomography (CT) scan and propagated to a rescan using deformable image registration (Mirada RTx). Dose distributions of the treatment plan were calculated on both images.
Replanning decisions are usually made by applying constraints to the recalculated dose on the rescan, using the warped structures. However, as a surrogate for recalculation, a dose projection method using a rigid translation applied to the original dose mapped onto the rescan was used. The same set of constraints was then applied to this resulting dose, in order to decide whether a replan was required. The results showed the automated dose projection method correctly removed 90 percent of cases from further evaluation while identifying 100 percent of those that required investigation. This indicates rigid dose projection onto rescan CTs is a fast and automated substitute for dose recalculation since full recalculation and replanning decisions need only be made on those patients flagged by the system.
The study forms part of Mirada’s Registration Assurance program, a comprehensive program for ensuring DIR quality and continuous improvement through rigorous scientific validation of technology, education, comprehensive QC tools and a commitment to ongoing development and support. The registration, contouring and adaptive replanning workflows used in the study are all available in the new releases of Mirada RTx and Mirada Workflow Box.
For more information: www.mirada-medical.com

 June 19, 2024
June 19, 2024