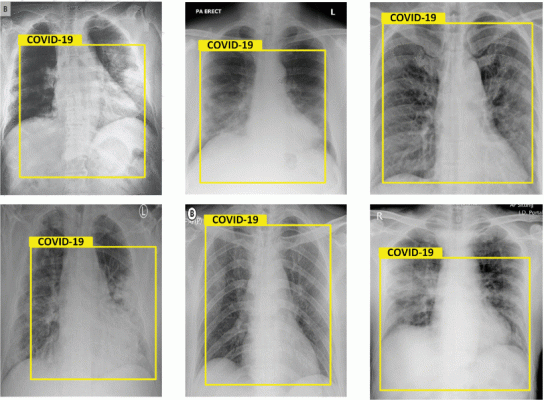
Results of chest X-Rays, detected as Covid-19. Images courtesy of IEEE
January 14, 2022 — The COVID-19 pandemic took the world by storm in early 2020 and has become since then the leading cause of death in several countries, including China, USA, Spain, and the United Kingdom. Researchers are working extensively on developing practical ways to diagnose COVID-19 infections, and many of them have focused their attention on how artificial intelligence (AI) could be leveraged for this purpose.
Several studies have reported that AI-based systems can be used to detect COVID-19 in chest X-ray images because the disease tends to produce areas with pus and water in the lungs, which show up as white spots in the X-ray scans. Although various diagnostic AI models based on this principle have been proposed, improving their accuracy, speed, and applicability remains a top priority.
Now, a team of scientists led by Professor Gwanggil Jeon of Incheon National University, Korea, has developed an automatic COVID-19 diagnosis framework that turns things up a notch by combining two powerful AI-based techniques. Their system can be trained to accurately differentiate between chest X-ray images of COVID-19 patients from non-COVID-19 ones. Their paper was made available online on October 27, 2021, and published on November 21, 2021, in Volume 8, Issue 21 of the IEEE Internet of Things Journal.
The two algorithms the researchers used were Faster R-CNN and ResNet-101. The first one is a machine learning-based model that uses a region-proposal network, which can be trained to identify the relevant regions in an input image. The second one is a deep-learning neural network comprising 101 layers, which was used as a backbone. ResNet-101, when trained with enough input data, is a powerful model for image recognition. "To the best of our knowledge, our approach is the first to combine ResNet-101 and Faster R-CNN for COVID-19 detection," remarked Prof. Jeon, "After training our model with 8800 X-ray images, we obtained a remarkable accuracy of 98%."
The research team believes that their strategy could prove useful for the early detection of COVID-19 in hospitals and public health centers. Using automatic diagnostic techniques based on AI technology could take some work and pressure off of radiologists and other medical experts, who have been facing huge workloads since the pandemic started. Moreover, as more modern medical devices become connected to the Internet, it will be possible to feed vast amounts of training data to the proposed model; this will result in even higher accuracies, and not just for COVID-19, as Prof. Jeon stated: "The deep learning approach used in our study are applicable to other types of medical images and could be used to diagnose different diseases."
For more information: www.inu.ac.kr/mbshome/mbs/inuengl/index.html
Related COVID Content:
COVID-19 Fallout May Lead to More Cancer Deaths
Kawasaki-like Inflammatory Disease Affects Children With COVID-19
FDA Adds Myocarditis Warning to COVID mRNA Vaccine Clinician Fact Sheets
CMS Now Requires COVID-19 Vaccinations for Healthcare Workers by January 4
Cardiac MRI of Myocarditis After COVID-19 Vaccination in Adolescents
Small Number of Patients Have Myocarditis-like Illness After COVID-19 Vaccination
Overview of Myocarditis Cases Caused by the COVID-19 Vaccine
Case Study Describes One of the First U.S. Cases of MIS-C
NIH-funded Project Wants to Identify Children at Risk for MIS-C From COVID-19


 December 05, 2025
December 05, 2025 









