If you enjoy this content, please share it with a colleague
RELATED CONTENT
UltraSPECT Inc. announced recently that Robert Wood Johnson Physician Enterprise (RWJPE), a multi-specialty, community-based physician group in Central New Jersey, implemented UltraSPECT’s Xpress3.Cardiac solution at four of their sites.
UltraSPECT Inc. announced the 10th anniversary of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of its Wide Beam Reconstruction (WBR) technology.
UltraSPECT Inc. has marked the 450th U.S. installation of its low-dose image processing technology for nuclear medicine. The milestone was reached as Firelands Regional Medical Center, Sandusky, Ohio, acquired Xpress3.Cardiac imaging solution to reduce radiation exposure for patients and staff and meet the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC) dose-reduction guidelines.
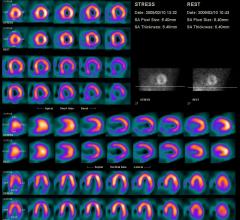
Nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) with positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) have been the gold standard for noninvasive detection of coronary ischemia and infarcts. However, the high radiation doses patients receive are making some providers think twice before referring their patients for nuclear MPI.
Public concern over radiation risks from medical imaging have been brought to the forefront with numerous mainstream media articles in recent years. Newer dose lowering technologies have helped reduce radiation dose by more than 50 percent for cardiac computed tomography angiography (CTA) scans, making it much more attractive as a diagnostic imaging modality. New CT technology — including perfusion imaging with advanced visualization software and CT-fractional flow reserve (FFR) imaging, recently cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) — may lead to increased use of CT.
When 64-slice scanners were first introduced nearly 10 years ago, CTA dose was 20-30 mSv, but new reconstruction software, more sensitive detectors and other technologies have reduced this below 10 mSv. With the newest scanners and software, it is now possible to perform CTA with about 1 mSv of dose. This new dose profile has made CTA much more attractive, and nuclear imaging now finds itself in the position as the high radiation dose technology being called into question.
BC Technical and UltraSPECT Inc. have entered into a long-term agreement to provide their customers easier access to UltraSPECT products across the nation.
The highest levels of radiation dose in medical imaging are reported in nuclear medicine and pressure is growing for lower dose.
UltraSPECT announced that MaineHealth, a family of hospitals and medical centers throughout Maine, has selected the UltraSPECT Xpress.Cardiac and Xpress3.Cardiac solutions as part of the organization’s strategy for reducing nuclear medicine (NM) dose and complying with the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC) final guidelines effective Jan. 1, 2014. Maine Medical Partners (MMP) – MaineHealth Cardiology in South Portland is one of ten facilities within MaineHealth that is installing the product, with others scheduled to continue roll out before the end of 2013.
UltraSPECT announced the installation of its proprietary Wide Beam Reconstruction (WBR) software at nearly 10 healthcare facilities. The installations came as a result of the recent agreement between UltraSPECT and radiopharmaceutical provider PharmaLogic, under which PharmaLogic offers the WBR software as part of its patient-centered approach.
UltraSPECT has announced its distribution agreement with PharmaLogic for the sale of UltraSPECT’s cardiac and bone imaging applications. The agreement will enable PharmaLogic to provide its hospitals and imaging centers with access to UltraSPECT’s Xpress line of products for lower radiation dose with no diminished image quality.
Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) remains a well-entrenched imaging modality for nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) more than 30 years after its introduction. Due to SPECT’s reliability, cost-effectiveness and the wealth of data showing its clinical validation, it remains more common in MPI than its competition, positron emission tomography (PET).


 July 25, 2016
July 25, 2016