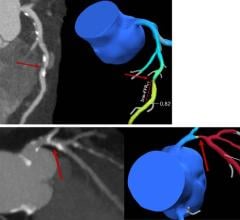
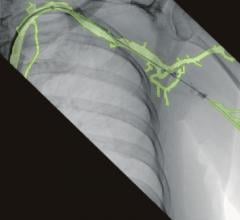
March 24, 2012 — Coronary angiography is unable to accurately predict the severity of vessel narrowing, suggesting fractional flow reserve (FFR) functional tests should be added to help determine if a patient needs revascularization. This was according to research presented from the IRIS FFR-DEFER trial at the American College of Cardiology's (ACC) 61st Annual Scientific Session this week in Chicago.
Seeking to improve physicians’ decision-making process when determining if a patient needs revascularization, a South Korean research team compared two different methods of evaluating arterial narrowing: coronary angiography and FFR. Currently, coronary angiography is commonly used to determine the need for revascularization, while FFR is included in practice guidelines but less frequently utilized. FFR uses an catheter probe to measure the level of blood flow before and after a stenotic lesion to determine how much the narrowing is affecting arterial function.
Specifically, the team wanted to determine why there is often a discrepancy, called a “visual-functional mismatch,” between the findings of these tests when performed on the same vessel.
“There are often notable discrepancies between the angiographic diameter stenosis and the physiologic significance of the lesion,” said lead investigator Seung-Jung Park, M.D., Ph.D., professor of medicine at Asan Medical Center in Seoul, South Korea.
“We conducted the study to provide a comprehensive understanding of the factors responsible for this ‘visual-functional mismatch,’ which we believed would be helpful to overcome interventionalists’ excessive preoccupation with using angiography to decide whether to treat or not to treat,” he said.
The researchers enrolled 1,000 patients with 1,129 lesions between November 2009 and June 2011 at a single center in Seoul, South Korea. Sixty-three patients had left main coronary artery (LMCA) lesions (a more complex type of narrowing; number of lesions=63), while 937 patients had non-LMCA lesions (number of lesions=1,066). The researchers completed three tests on each lesion: coronary angiography, FFR and intravascular ultrasound. They then examined the occurrence of visual-functional mismatch and analyzed the factors that led to the discrepancies between coronary angiography and FFR.
They found that among patients with non-LMCA (less complex) lesions, there were 605 lesions in which coronary angiography showed that the vessel had narrowed by more than 50 percent (suggesting that the heart may not be getting enough oxygen, a condition called “myocardial ischemia”). Of these lesions, 343 (57 percent) showed a FFR of greater than or equal to 0.80 (no more than a 20 percent reduction in blood flow, suggesting that ischemia was unlikely), resulting in a visual-functional mismatch.
Conversely, among the 461 non-LMCA lesions with less than or equal to 50 percent vessel narrowing (suggesting that ischemia was unlikely), 75 (16 percent) had an FFR of less than 0.80 (more than a 20 percent reduction in blood flow, suggesting that ischemia was likely), resulting in a “reverse” visual-functional mismatch.
In the LMCA group, mismatch was seen in 8 lesions (35 percent). Reverse mismatch was seen in 16 lesions (40 percent).
Using statistical analysis and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), the researchers determined several factors that were predictors of mismatch, including: older patient age (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] 1.04, p<0.001), non-left anterior descending artery location (AOR 3, p<0.001), the absence of plaque rupture (AOR 2.6, p=0.004), short lesion length (AOR 1.03, p<0.001), a large minimal lumen cross-sectional area (AOR 2, p=0.001), a smaller plaque burden (AOR 1.05, p<0.001) and a greater minimal lumen diameter (AOR 1.09, p=0.040).
The predictors of reverse mismatch included younger age (AOR 1.04, p=0.003), left anterior descending artery location (AOR 5.4, p<0.001), the presence of plaque rupture (AOR 3.2, p=0.011), smaller minimal lumen cross-sectional area (AOR 2.9, p<0.001) and larger plaque burden (AOR 1.03, p=0.027).
According to the researchers, the results showed that discrepancies between the two tests were caused by clinical and lesion-specific factors that are often unable to be identified from coronary angiography alone. They concluded that coronary angiography could not accurately predict the functional results of FFR and that FFR should be included in the assessment process before cardiac specialists make decisions about revascularization.
For more information: www.acc.org






 May 17, 2024
May 17, 2024