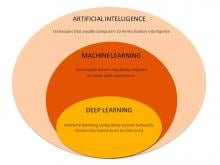
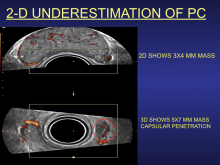
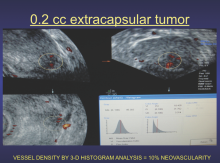
The use of smart algorithms has the potential to make healthcare more efficient. Sarah Eskreis-Winkler, M.D., presented data that such an algorithm — trained using deep learning (DL), a type of artificial intelligence (AI) — can reliably identify breast tumors in magnetic resonance (MR) images. In doing so, the algorithm has the potential to make radiology more efficient.
If you enjoy this content, please share it with a colleague
- Read more about AI Algorithm Detects Breast Cancer in MR Images
- Log in or register to post comments