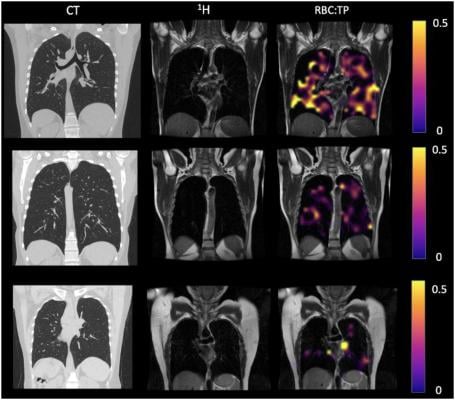
Example CT, proton, proton and RBC:TP imaging from post-Covid-19 condition participants. The top row is a participant with RBC:TP = 0.49, the middle row is a participant with RBC:TP of 0.31, and the bottom row is a participant with RBC:TP = 0.24. Imaging showed little to no discernible damage on CT, and yet highly heterogeneous and low RBC:TP in the lungs of non-hospitalized post-Covid-19 condition participants. RBC:TP = Hyperpolarized 129Xenon MRI lung ratio of red blood cell spectral peak to tissue phase spectral peak. Image courtesy of the Radiological Society of North America
May 24, 2022 — A special type of MRI found lung abnormalities in patients who had previously had COVID-19, even those who had not been hospitalized with the illness, according to a new study published in the journal Radiology.
“In a collaboration between the University of Oxford and the University of Sheffield, we have been able to identify abnormalities in the lungs of both hospitalized and non-hospitalized participants using a novel imaging technique, Hyperpolarized Xenon 129MRI, or Hp-XeMRI,” said the study’s senior author, Fergus Gleeson, M.B.B.S., from the Department of Oncology, University of Oxford and Department of Radiology, Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust. “These abnormalities are not apparent on conventional imaging, and in some individuals were detected up to a year after their initial COVID-19 infection.”
Beyond the acute respiratory symptoms of COVID-19 infection, which can result in severe illness, hospitalization and death, the medium and long‐term problems experienced by people following COVID‐19 can be considerable. Symptoms can persist months after initial infection. The presence of ongoing symptoms related to prior COVID-19 infection is known as post-COVID-19 condition, or long COVID. Although over 200 symptoms have been reported, the most common are breathlessness, fatigue and brain fog. Long COVID presents a global health burden, with many people unable to return to normal activities or employment months after becoming unwell.
Hp-XeMRI has shown promise in detecting abnormalities of alveolar gas exchange—where oxygen moves from the lungs to the bloodstream and carbon dioxide passes from the blood to the lungs—even when CT scans and lung function tests were normal. Hp-XeMRI enables the assessment of ventilation and gas exchange into red blood cells. It provides regional information of pulmonary vasculature integrity and may be able to identify lung abnormalities not apparent on CT.

3D render of full-scale airway network modelling analysis (FAN) (A), FAN modelling (B), and hyperpolarized Xenon imaging (C, D) in both non-hospitalized post-Covid-19 condition and post-hospitalized COVID-19 participants. Results from both the low-resolution and ventilation imaging are similar and did not correlate with clinical or dissolved phase imaging results. Image courtesy of the Radiological Society of North America
In long COVID, a breathing pattern disorder is commonly identified and contributes to breathlessness in a significant proportion of patients. However, whether there are additional reasons for their breathlessness remains unclear.
“Using Hp-XeMRI may enable us to further understand the cause of breathlessness in long COVID patients, and ultimately lead to better treatments to improve this often debilitating symptom,” said study co-author James T. Grist, Ph.D., from University of Oxford Centre for Clinical Magnetic Resonance Research, and the Department of Radiology at Oxford University Hospitals NHS Trust.
For this prospective study, researchers set out to determine whether previously described lung abnormalities on Hp-XeMRI in post-hospitalized COVID-19 participants are also present in non-hospitalized participants with long COVID.
Eleven non-hospitalized long COVID (NHLC) participants and 12 post-hospitalized COVID-19 (PHC) participants were enrolled from June 2020 to August 2021. All participants had symptoms of breathlessness. NHLC participants were 240-334 days from infection, and PHC participants were 105-190 days from infection. As a control group, healthy volunteers with no evidence of prior COVID-19 infection were recruited from staff at the University of Sheffield and the University of Oxford.
Participants were given chest CT, Hp-XeMRI, pulmonary function tests, one-minute sit-to-stand tests and breathlessness questionnaires. Control subjects underwent HP-XeMRI only. CT scans were analyzed for post-COVID lung disease severity using a previously published scoring system, and Full-scale Airway Network (FAN) modelling. Analysis used group and pair-wise comparisons between participants and controls, and correlations between participant clinical and imaging data. NHLC and PHC participants had normal or near normal CT scans.
“We saw that the ability of gas to transfer from the lungs into the blood stream was less in non-hospitalized patients in comparison to those hospitalized with COVID,” Dr. Gleeson said. “Furthermore, both groups of participants had lower dissolved phase Hp-XeMRI values than healthy participants, pointing to potential defects in either the lining of the lung or the surrounding blood vessels.”
The results showed that there were significant differences in mean red blood cell to tissue plasma ratio between healthy controls and PHC/NHLC participants, indicating potential differences in lung function.
Although participants had normal or near normal CT scores, total lung diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide percentage was significantly lower between NHLC and PHC participants, potentially indicating a decrease in lung function but not structure.
The researchers said their next step is to expand their study to look at larger numbers of participants seen in dedicated post-COVID clinics at four U.K. centers.
“We will assess different groups of participants who have had COVID and correlate the findings with physiological data, symptom-based questionnaires and cardiac MRI to better understand the clinical significance of our findings,” Dr. Gleeson said. “Further work to delineate the nature of the abnormality will also be undertaken which will then enable us to determine whether specific treatments may be beneficial.”
In the meantime, the researchers offer advice for those currently coping with the symptoms of long COVID.
“Although we have much to learn about the biological mechanisms underlying long COVID, the benefit of practical strategies, such as breathing control exercises and fatigue management should not be underestimated and are helping many patients struggling with lingering symptoms,” Dr. Grist said. “Seeking help from your primary care doctor can help support your recovery.”
For more information: www.rsna.org
Related Long-COVID Content:
MRI Sheds Light on COVID Vaccine-Associated Heart Muscle Injury
What We Know About Cardiac Long-COVID Two Years Into the Pandemic
VIDEO: Long-term Cardiac Impacts of COVID-19 Two Years Into The Pandemic — Interview with Aaron Baggish, M.D.
VIDEO: Long-COVID Presentations in Cardiology at Beaumont Hospital — Interview with Justin Trivax, M.D.
VIDEO: Cardiac Presentations in COVID Long-haulers at Cedars-Sinai Hospital — Interview with Siddharth Singh, M.D.
Find more COVID news and videos
PHOTO GALLERY: How COVID-19 Appears on Medical Imaging
VIDEO: How to Image COVID-19 and Radiological Presentations of the Virus — Interview with Margarita Revzin, M.D.


 December 04, 2025
December 04, 2025 









