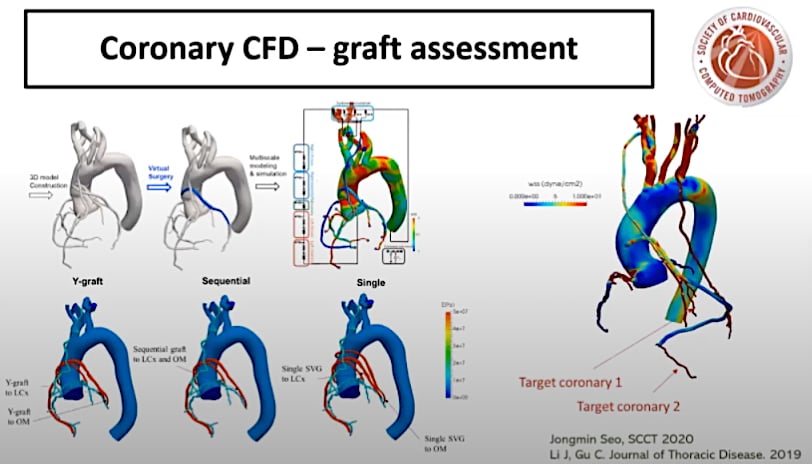
Sheer stresses on the walls of arteries are believed to cause the formation atherosclerotic plaques. This is an area of research that is expected to see increased use in the next few years. This study was presented at SCCT 2020 as an example of how sheer stresses can help evaluate and predict the patency of coronary artery bypass grafts (CABG).
The latest technical advances and trends in computed tomography (CT) and the latest clinical study data were discussed at the Society of Cardiovascular CT (SCCT) 2020 virtual meeting in July. Hot topics included quantification of low-attenuation coronary plaque as the next big cardiac risk assessment, coronary artery shear stress as a marker for heart attacks, CT for the assessment of non-STEMI patients, the role of CT in COVID-19, CT's role in structural heart assessments, as well as new CT technologies.
COVID Impact on Cardiology and Radiology and the Role of CT in the Pandemic
"The role of CT and cardiology in COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) is still very much to be learned in the midst of this pandemic," explained SCCT Vice President Ed Nicol, M.D., MBA, FSCCT, Royal Brompton and Chelsea and Westminster Hospitals, London, who offered an overview of the key takeaways from SCCT 2020 in the closing session. However, he said CT has emerged as one of the primary imaging modalities in the COVID era.
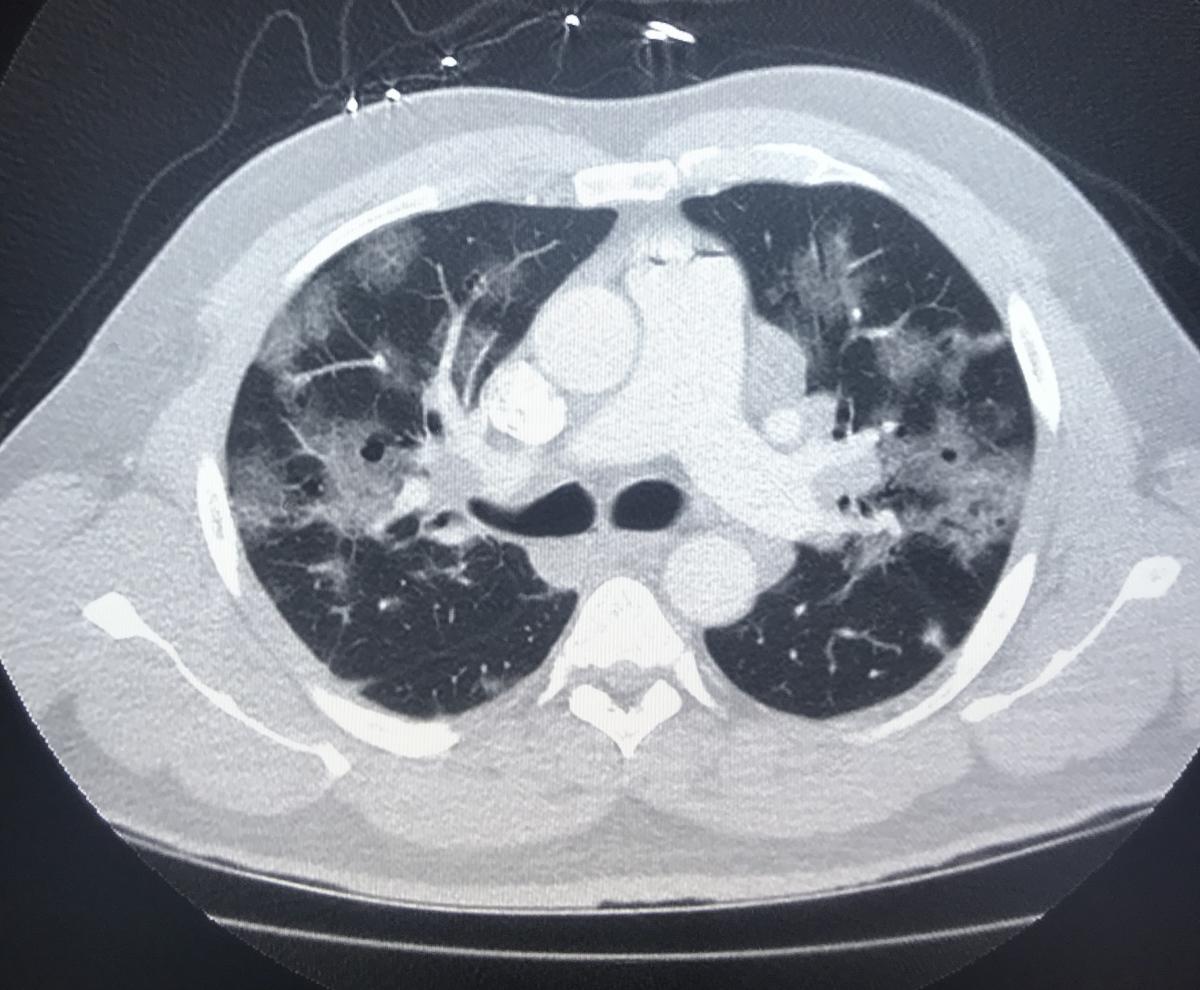 He noted CT can be used to evaluate chest pain, etiology of LV dysfunction, new onset of heart failure or cardiomyopathy, evaluation of patients with possible angina and new arrhythmias. And, unlike echocardiography, it does not require clinicians to be in close proximity to patients being scanned. CT exams are also fast, helping reduce the exposure time spent with patients.
He noted CT can be used to evaluate chest pain, etiology of LV dysfunction, new onset of heart failure or cardiomyopathy, evaluation of patients with possible angina and new arrhythmias. And, unlike echocardiography, it does not require clinicians to be in close proximity to patients being scanned. CT exams are also fast, helping reduce the exposure time spent with patients.
"When you reflect on what the question is that is being asked, in the era of COVID, more than ever, COVID really needs to serve as a crucible for change in imaging. We need to be removing the layering of testing whenever possible, and we should avoid invasive testing when at all possible," said Jonathon Leipsic, M.D., MSCCT, chairman of the department of radiology for Providence Health Care, Vancouver Coastal Health and the vice chairman of research for the University of British Columbia Department of Radiology. He spoke in a session on CT use during the COVID era. "Historically, we may have wanted to do two tests, but perhaps now we have to consider getting by with only one, and one that does not involve invasive procedures or risk of aerosolizing."
He cited a July paper in JACC Cardiovascular Imaging,[1] which he was a co-author, that cites the dangers of imaging patients in the COVID era and states that it is time to consider making changes to the practice before returning to "normal" imaging workflows. The article strongly suggests not using transesophageal echo (TEE) if other modalities such as CT can be used, and to look for alternatives for exercise stress.
"If you look at the text you can see across all these associate editors real thought leadership from the MR, nuclear and echo community, there was still in the text a clear emphasis that cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA) might have distinct advantages in the deceleration phase of the coronavirus pandemic for increased efficiency, safety and resource utilization," Leipsic said.
He said this is especially true of identifying coronary disease patients that can be treated conservatively. This includes excluding patients with high risk anatomy or through the use of fractional flow reserve CT (FFR-CT) to exclude functionally significant lesions.
While a big proponent of cardiac CT angiography (CCTA), Leipsic said we still need to follow the guidelines, which includes not using CCTA in the setting of known disease, extremes in calcium scores or in patients with poorly controlled heart rate.
Low-attenuation Plaque Burden Will Become Next Big Risk Assessment
Several speakers at SCCT mentioned the use of CTA to examine the type of atherosclerotic plaques inside the coronary vessels to determine the patient's risk for a heart attack. CT has the ability to determine the types of plaque based on the Hounsfield value of the pixels that make up the plaque. Low-attenuation plaque (LAP) has been implicated as a a risk factor for unstable plaques (vulnerable plaques) that irritate the vessel walls and cause a rupture, leading to the formation of a clot at the site and causing a myocardial infarction (MI).
The trial that had many people talking was the SCOT-HEART Trial: LAP Burden sub-study.[2] It showed non low attenuation, noncalcified plaque accurately predicts MI. The study found there was a five-fold increase in MI if LAP was above 4 percent.
Classifying plaque can be tedious to characterize manually and subject to reader variability, so this study used a semi-automated artificial intelligence (AI)-based plaque quantification software to standardize how the plaque was analyzed.
"It's really the low-attenuation plaque burden that is the strongest predictor MI, above and beyond calcium scoring, and this is really the first him that has been shown. The study had a relatively low number of events, but a very strong signal in the data," Nicol explained.
The findings were further reinforced by the PARADIGM Trial.[3] The study looked at high-risk plaques and found these were the main drivers for subsequent MIs. This has prompted discussion around revising the current CAD-RAD scores used by cardiologists and radiologists to systematically grade a patient's cardiovascular risk for events based on plaque burden severity.[4]
Read more on low-attenuation plaque risk assessments
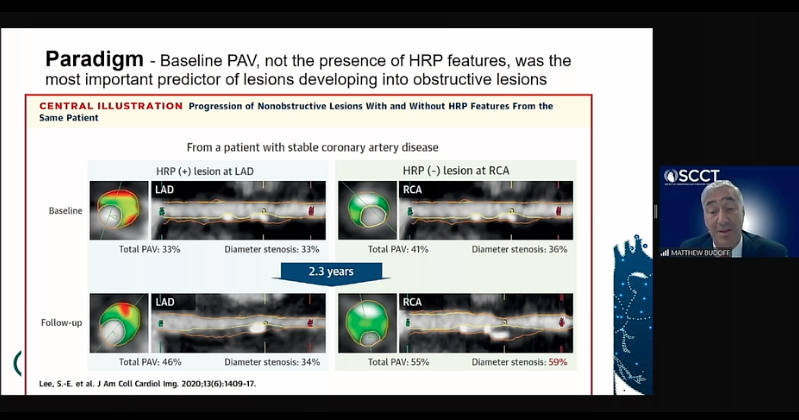
CT coronary plaque assessment software used in the PARADIGM trial showed low attenuation plaques are a more important predictor of cardiac events than calcium scores. Here the trial data is being presented at SCCT 2020 by Matthew J. Budoff, M.D., FACC, professor of medicine at the David Geffen School of Medicine, and director of cardiac CT Harbor-UCLA Medical Center.
Coronary Artery Shear Stress as a Marker for Heart Attacks
Another risk assessment tool, measurement of coronary artery shear stress from blood flow, which has been discussed academically for years, is starting to see use in clinical studies. One study from the past year looked at the use of FFR-CT to use sheer stresses as a prediction tool for plaque rupture and acute coronary syndromes.[5] The study used the computational fluid dynamics data from FFR-CT to look at the sheer stresses along the vessel walls predict future events.
Nicol said sheer stress computational fluid dynamics is already being used at some centers to assess coronary grafts. In one study Nicol cited, flows to coronary arteries were assessed by determining coronary resistance.[6]
Novel Cardiac CT Technologies
New software is allowing for perivascular fat attenuation index (FAI) evaluation to further enhance coronary plaque evaluations and allow more precise classification. It color-codes the Hounsfield FAI values to make the details and assessment easier. Serial images of the plaque using this technique allows visualization of fat changes in the vessel, showing improvement or worsening with use of statins, for example.[7]
"I think this might change the way we view coronary anatomy moving forward," Nicol explained.
He shared a slide from a study using the technique to evaluate psoriasis treatments from a National Institutes of Health and Oxford collaboration. The study showed a clear response to drug treatments compared to the control group.[8]
Another new advancement is photon-counting CT scanners, which will allow for much improved spacial resolution, reduction of artifacts and simultaneous multi-energy acquisition at the same time for spectral imaging to analyze material composition in the image.[9,10,11]
"This is be a big next-step change in CT technology," Nicol said. "While complex, I think it has a lot of potential moving forward and we will see more of in the future."
AI Applications in Cardiac CT
Machine learning is also starting to have an impact on cardiac CT imaging, helping speed workflows in post-processing of images. "It's being used for segmentation, whether that is for coronary vessels or cardiac structures, it is being used to predict calcium scores in a fraction of a second," Nicol said.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being applied to radiomics, where the machine can sift through vast amounts of imaging data to discover hidden patterns that show imaging derived traits that can be used as predictors for disease. He noted radionics studies to identify patients at high risk for myocardial infarctions based solely in imaging data that goes beyond the usually anatomical information on plaque or calcium in coronary vessels. However, he said this growing area of research will require radiologists and cardiologists to learn a new way of looking at things and to understand the algorithms involved, because the science is outside the usual scope of their training.
Deep learning algorithms are already commercially available for hybrid CT image reconstruction, but are also being applied to how epicardial fat can be used for long-term prognosis, automation of calcium scoring using non-contrast CT, and how to improve calcium scoring reporting for non-gated CT scans, including scans used for cancer treatment planning or lung screenings.
AI is also being applied for the automatic analysis of endocardial architecture and strain. Nicol said this includes enabling full heart myocardial strain imaging in a single heartbeat, eliminating the need for the user to draw contours, and can be done in a highly reproducible manner, even at high heart rates.[12]
CT To Assess Therapy for Non-STEMI Patients
CT is not usually associated with use in evaluating patients with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, but two studies from the past year, CARMENTA and VERDICT, looked at this. Both found CTA can help determine if if a patient should be sent for a diagnostic angiogram, or if a non-invasive exam is good enough to determine if revascularization is needed.[13,14]
"This is very relevant as we try to reduce the number of invasive coronary angiograms in a COVID-19 environment," he explained.
What to do About Hyper-attenuated Leaflet Thickening In Replacement Valves
Hyper-attenuated leaflet thickening (HALT) on CT imaging due to thrombus formation on the valve leaflets has been a big concern since it was discovered a few years ago in the Abbott Portico transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) trial. It was subsequently found in all commercially available TAVR and surgical valves. The big question has been if this is benign or if patients should be given anticoagulants.
"This is an area of major interest over the past couple of years. Things now might be becoming clearer, with it being similar in both surgical and transcatheter valve replacements with a relatively high prevalence. But, I still don't think it is clear exactly what it means or how it should be treated," Nicol said. "We are still unclear of the clinical significance of this condition and I think it is watch and wait area."
Nicol cited a couple recent studies that note CT is the gold standard for assessing this condition and that HALT rates are similar between TAVR and SAVR, and occurs in about 10-45 percent of patients.[15,16]
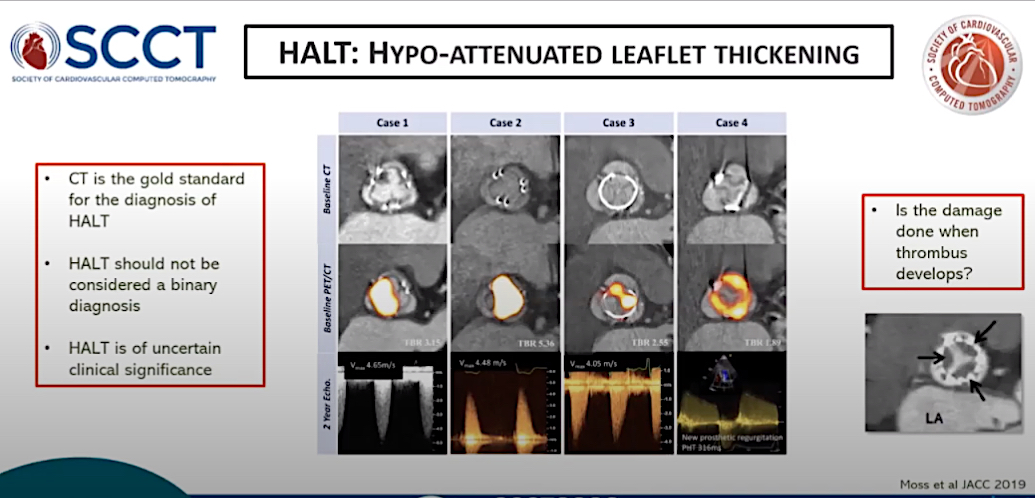
Hyper-attenuated leaflet thickening (HALT) on CT imaging due to thrombus formation on the valve leaflets has been a big concern but data from several studies shows it appears to be benign. This slide is from one of the HALT studies presented by SCCT Vice President Ed Nicol, M.D.
CT for Structural Heart Assessments
CTA is the gold standard for patient selection screening and pre-procedural planning for TAVR and is now playing that same key role in the growing area of transcatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR) and more advanced structural heart assessments. The imaging is used to make scores of measurements to assess access routes, calcification, valve annulus size and shape, assessing if there will be any obstructions to the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT).
LVOT assessments are now done in most patients receiving a TAVR valve for the mitral position, which includes software for virtual placement of a valve to examine how it fits and will impact flow within left ventricle. Nicol said this evaluation can help determine if adjunct techniques are required to increase flow and prevent obstruction, including the use of alcohol septal ablation or the LAMPOON procedure.
CT is now being used routinely for prosthetic valve followup exams to assess leaflet motion, valve obstruction due thrombus vegetation or subprosthetic pannus, paravalvular leaks and to detect infective endocarditis.
A new area of study is CT quantification of myocardial extracellular volume to identify occult transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis (ATTR) in patients being considered for TAVR.[17]
In left atrial appendage (LAA) occlusion, CT pre-planning imaging is used to assess valve size and LAA shape and two determine the optimal landing zone for transeptal punctures for occluder delivery. But Nicol said new computational modeling software technology is now enabling virtual device placement to better assess sizing, device selection and optimal landing zones to prevent embolization.[18]
Transesophogeal echo (TEE) is included in the guidelines and is what is traditionally used to assess the the LAA for occlusion, but recent studies show CT may be better suited for the task, Nicol said.[19]
"The guidelines unfortunately really don't live up to the data that is increasingly being published, particularly in terms of the long-term followup, where I would argue CT has some advantages in terms of our ability to look at any plane and at a level of spacial and temporal resolution that is probably unmatched with other techniques," he explained.
CT is also being used increasing in uncommon niche structural heart applications, Nicol said. This includes ischemic ventricular septal defect (VSD) closure assessments[20] and left ventricular assist device (LVAD) assessments. For LVADS, CT can identify thrombus formation and the cause of pump issues, allow functional flow cine imaging, view mechanical complications and look at outflow and inflow issues.
Use of CT in Congenital Heart Evaluations
Cardiac CT has an increasing role in congenital heart disease assessments and is now included in the new joint society guidelines issued by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) earlier in 2020.[21] One of the main roles is to help guide atrial septal defect (ASD) and VSD device closures.
Calcium Scoring Added to Guidelines as Primary Cardiac Risk Assessment
The use of CT coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring tests offers a fast, inexpensive and non-invasive exam to assess patient risk for coronary artery disease (CAD). It has been a topic of discussion at SCCT for years, but in the past year, more centers are now using this as a standard of care with CAC now being included in recorded screening guidelines by several cardiovascular organizations.
Nicol said CAC offers a "warranty period" for no cardiovascular events for patients who show a score of zero, which is known as "the power of zero." He said recent studies also have reinforced the use of CAC scoring to determine which patients should be treated with statins and aspirin, and can be used to personalize treatments to individual patients.[22,23,24]
Cardiovascular CT (CCT) is comprehensive, with one exam that enables anatomical imaging, functional imaging, coronary plaque characterization, CCT-FFR and stress perfusion.
Cardiac CT Reimbursements Declines Evidence for their Use Increases
While clinical studies continue to show new evidence that CTA is cost-effective, can speed diagnosis and offer a variety of tools to assess patients, Nicol said SCCT has documented a 31 percent decrease in the reimbursement rates over the past three years.
"In the U.S., there is a worry about this trend. The SCCT advocacy team is working hard to try and make sure that this trend does not prevail and that mayors really understand the value of coronary CT angiography," Nicol said.
References:


 December 10, 2025
December 10, 2025 








