
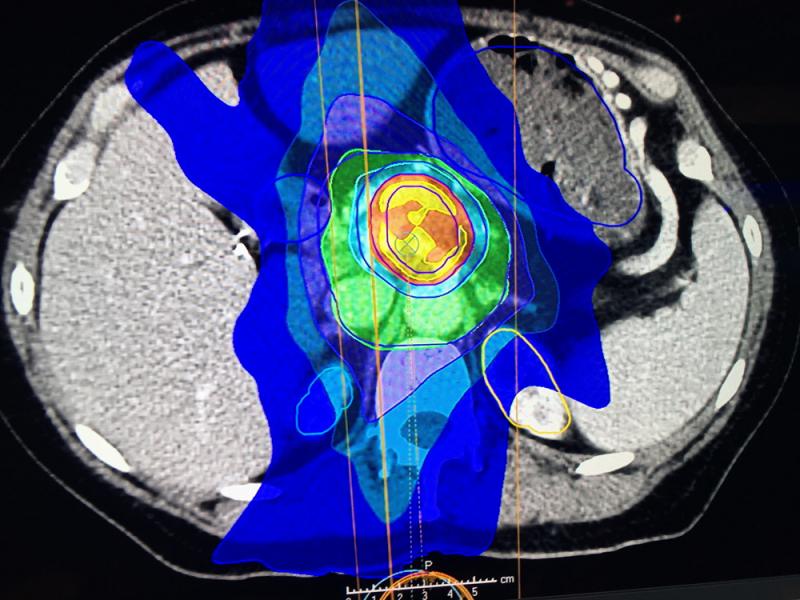
Varian received FDA clearance for its Ethos therapy in February 2020, shown here displayed for the first time at ASTRO 2019. It is an adaptive intelligence solution that uses onboard AI in the treatment system to take the cone beam CT imaging on the system, compare it to the treatment plan and deliver an entire adaptive treatment plan in a typical 15-minute treatment time slot, from patient setup through treatment delivery.
The traditional treatment planning process takes days to create an optimized radiation therapy delivery plan, but new artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are helping speed this process. In some cases autonomous AI-generated plans can be generated in a couple minutes.
"AI can help treatment planners and dosimetrists by saving a lot of time doing simpler, repetitive tasks that you do again and again, now the AI can do that for you and you can spend your time on those more challenging, difficult cases and you can do a better job there," explained Steve Jiang, Ph.D., director of the medical artificial intelligence and automation lab and vice-chair of the Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Texas Southwestern.
Artificial Intelligence in Radiation Oncology Treatment Planning
Varian and RaySearch have both developed machine-learning technologies to automate treatment plans.
"The fully automated system takes in the patient imaging and the target defined by the physician, and out on the other end comes a fully deliverable therapy plan," said Kevin Moore, Ph.D., DABR, deputy director of medical physics and associate professor, University of California San Diego, who is using the Varian AI TSP software.
He said UCSD began using the software in tandem with traditional treatment planning to ensure the plans were as good as human created plans. After a human-made plan was completed, he said they ran the AI and it took 5-20 minutes to complete a plans start to finish depending on the complexity. "The comparisons were very good," Moore said. The site is now running the AI treatment plans first and and the human planner looks at it to see if it can be further optimized.
The system has helped with speed and efficacy at UCSD Moore said, and the site has now treated well over 1,000 patients with its AI-assisted planning.
Machine learning was incorporated into the RaySearch 8B TPS in 2018 and began it began to be used clinically in 2019. The system is trained to take the treatment planning computed tomography (CT) scan and automatically segment the anatomy and auto contour to help speed the planning process.
Princess Margaret Cancer Center, part of the University Health Network in Toronto, Canada, was an early adopter of AI-based treatment planning in 2019. The center conducted a study where it used the RaySearch machine learning treatment plan system to automatically generate plans along side traditional human made plans. The radiation oncologist then compared the two plans to decide if they are acceptable and which is their favorite plan.
"The automated treatment planning system works by training the algorithm with curated sets of similar treatment plans and it is able to detect the patients who are most similar to a novel patient and create a new treatment plan for that patient with no user interaction, beyond pressing the play button," explained Leigh Conroy, Ph.D., physics resident, at Princess Margaret Cancer Center, who has been working on the AI implementation.
She said the machine-generated plan can be modified and optimized by the human planners before being sent to the therapy system. The center began using the system clinically last summer.
Some plans are easier to create than others, so Conroy said the AI system might be used to help free up treatment planners to work on more complex cases, such as head and neck.
The RayStation 8B TPS software can be trained to automate treatment planning as well as organ segmentation, either using the clinic’s own data or by pre-trained models provided by RaySearch.
RaySearch is developing several other machine learning applications, including target volume estimation and large-scale data extraction and analysis.
Adaptive AI-Driven Onboard Planning in the Radiotherapy System
Varian received FDA clearance for its Ethos AI-driven radiation therapy system in February 2020. It is an adaptive intelligence solution that uses AI in the treatment system to take the onboard cone beam CT imaging and compare it to the treatment plan and deliver an entire adaptive treatment plan in a typical 15-minute treatment time slot, from patient setup through treatment delivery.
Tumors change position and size during a course of radiotherapy treatments. Changes in anatomical positioning that move tumors outside TPS margins also occur due to weight loss, position of the uterus, how full the bladder is, and intestinal gas, explained David Sjostrom, Ph.D., deputy chief physicist, Herlev Hospital, Department of Oncology, Division of Radiotherapy, Herlev, Denmark. He had the first clinical experience treating patients with the Varian Ethos system in September 2019.
"Normally it would take days to modify a treatment plan, and you don't do that online with the patient on the table. What we have done up until today was treating within the margins of the plan, or maybe had a study where we had different selections of plans, but it is still not the optimal way of doing it," Sjostrom said.
"So you would have a plan for a small bladder, a medium sized bladder and a large bladder, but what if it is anything in between? With the AI drive workflow, we now get results where we don't need to edit anything and that is the beauty," he explained.
Sjostrom said the system takes a couple minutes to create the plan and then it can be compared to the original plan and you can tell the system which one you want to use, or you can modify one of the plans. However, Sjostrom said so far they have picked the AI generated plan without modification. He said they have averaged a 40 percent reduction in the target margins using the AI-based system.
AI Auto Contouring for Treatment Plans
In early 2018, Mirada Medical received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance for the world’s first AI-powered auto-contouring solution. The DLCExpert software automatically contours of computed tomography (CT) scans based on next-generation deep learning contouring (DLC) and is now in use in multiple academic medical centers worldwide.
The DLCExpert deep learning software automatically identifies organs, segments and auto-contours them as the first step in creating radiation oncology treatment plans without any human intervention. The files created by the software are vendor neutral and can be imported into any vendor’s treatment planning system.
Siris Medical also gained FDA clearance in 2018 for its AI-driven, real-time editing of plan contours in its PlanMD decision support software. As the user draws the contours of the target treatment area, the software lets the user see the result of their efforts in real time, without re-optimizing or replanning, which can lead to significant time savings. A newer version of the software was released in January 2019.
The PlanMD software is a complement to Siris’ other AI product, QuickMatch, which automatically pulls up prior cases from its archive that are most similar to the current one. Once the QuickMatch algorithm has been properly trained, it can reduce the time required for treatment planning by up to 70 percent, according to the vendor.
AI May Be Used to Create MRI-derived CT Scans for Planning
As radiation oncology moves toward use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) radiotherapy treatment systems because of the better soft tissue delineation and ability to provide real-time imaging during treatment, AI will play a role to help eliminate the need for CT scans. CT is the basis for all current treatment planning because the radiation absorption of various tissues can be calculated from the Hounsfield units of the image grayscales that makeup the image. So all plans, even MR-guided Linacs, require CT imaging for treatment planning.
However, AI can create MRI-derived CT-like image reconstructions for treatment planning and eliminate the need for CT exams, Jiang explained. He said this can help reduce costs and save hospital resources. Eliminating CT scans also can help speed the planning process and reduce patient wait times for treatment, he said.
Related AI Treatment Planning Content:
VIDEO: Artificial Intelligence Driven Adaptive Radiotherapy System Begins Treating Patients — Interview with David Sjostrom, Ph.D.
VIDEO: Artificial Intelligence Automatic Contouring and Segmentation For Radiotherapy
New Treatment Planning System Technologies
VIDEO: Real-world Implementation of Deep Learning for Treatment Planning — Interview with Kevin Moore, Ph.D.
VIDEO: Varian Showcases Latest Developments at ASTRO 2019
Top Technology Trends at ASTRO 2018
Varian Receives FDA 510(k) Clearance for Ethos Therapy
VIDEO: The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Radiation Therapy — Interview with Steve Jiang, Ph.D.


 December 04, 2025
December 04, 2025 








