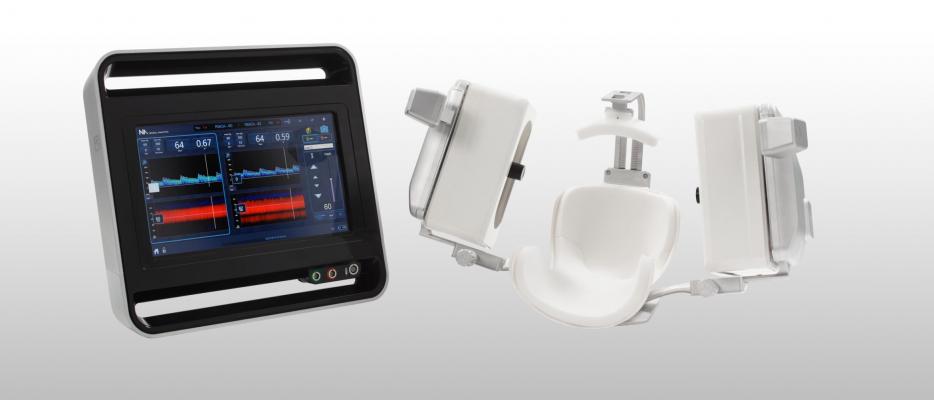
July 3, 2018 — Medical robotics company Neural Analytics Inc. announced that it received CE Mark for its NeuralBot System, a robotic assistance technology which automatically adjusts orientation and position of its ultrasound products under the guidance of a healthcare professional. The system has also received 510(k) clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). When used with its previously cleared Lucid M1 Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound System, it can assist clinicians to non-invasively monitor a patient’s brain blood flow characteristics and can provide information to diagnose a variety of neurological disorders.
“This technology allows us to look inside the brain, evaluate blood flow characteristics and track emboli in patients. It provides us with critical information on brain health in real-time to help us diagnose neurological disorders, prior to the need for additional, more invasive testing,” said Prof. Claudio Baracchini, M.D., FESO, director of the Stroke Unit and Neurosonology Lab at the University of Padua (Italy) and president of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics (ESNCH).
In April, at the 23rd ESNCH Meeting in Prague, Neural Analytics presented research data that demonstrated there was no statistical difference between ultrasound blood flow data collected with its NeuralBot System or data collected manually by an expert technician with its traditional ultrasound platform.(5)
The worldwide prevalence of stroke in 2010 was 33 million cases, with 16.9 million people having their first stroke.(1) Stroke claims a life every five seconds and is the second most common cause of death accounting for over 11.9 percent total deaths worldwide.(2) The burden of disease caused by stroke is set to double worldwide by 2030.(3) The number of stroke events in Europe is projected to rise from 1.1 million to 1.5 million per year by 2025.(4) Stroke is a time sensitive disease and requires intervention within 24 hours of onset of symptoms. Incorrect assessment of large vessel stroke leads to misdiagnosis and treatment delays, resulting in death or disability for stroke patients. Despite recent advances in life-saving treatments for acute ischemic stroke, less than 5 percent of stroke patients qualify for intervention because they do not present early enough.(6)
Neural Analytics will immediately commercialize the NeuralBot System with its currently available Lucid M1 TCD System in Europe as the ‘Lucid Robotic System’.
For more information: www.neuralanalytics.com
References
(1) Lozano R, Naghavi M, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. The Lancet. 2012;380:2095–2128.
(2) World Health Organisation. (2014). The top 10 causes of death. Available: http://www.who. int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/ int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/.
(3) Feigin VL, et al. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990-2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. The Lancet, Early Online Publication, 24 October 2013
(4) T. Truelsena, et al. Stroke incidence and prevalence in Europe: a review of available data. European Journal of Neurology. 2006,13: 581–598
(5) Fully Automated Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound Insonation of the MCA using 5 Degree of Freedom Robotically Actuated Probe System
(6) Christopher R. Bernheisel, MD, Jeffrey D. Schlaudecker, MD, Katelyn Leopold, MD. Subacute Management of Ischemic Stroke. American Family Physician, 2011 Dec 15;84(12):1383-1388


 April 16, 2025
April 16, 2025