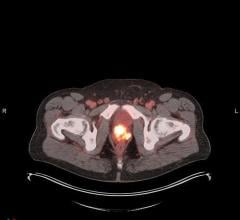
SPECT/CT reconstructions and VOIs used for determination of calibration factors for the adult kidney filled with Lu-177 (A) and the corresponding sphere filled with I-131 (B). Credit: University of Würzburg
January 6, 2017 — In nuclear medicine, the goal is to keep radiation exposure at a minimum, while obtaining quality images. Optimal dosing for individual patients can be difficult to determine. That’s where 3-D-printed organ models of varying size and shape could be of great use.
In a study reported in the December issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, researchers at the University of Würzburg in Würzburg, Germany, demonstrated that low-cost 3-D printing technology can be used for clinical prototyping. Johannes Tran-Gia, Ph.D., the study’s corresponding author, explained, ‟This research shows a way of producing inexpensive models of patient-specific organs/lesions for providing direct and patient-specific calibration constants. This is particularly important for imaging systems suffering from poor spatial resolution and ill-defined quantification, such as SPECT [single photon emission computed tomography]/CT.”
To demonstrate the potential of 3-D printing techniques for quantitative SPECT/CT imaging, kidneys — as organs-at-risk in many radionuclide therapies — were selected for the study.
A set of four one-compartment kidney dosimetry phantoms and their spherical counterparts with filling volumes between 8 mL (newborn) and 123 mL (adult) were designed based on the outer kidney dimensions provided by Medical Internal Radiation Dose (MIRD) guidelines. Based on these designs, refillable, waterproof and chemically stable models were manufactured with a fused deposition modeling 3-D printer. Nuclide-dependent SPECT/CT calibration factors for technetium-99m (Tc-99m), lutetium-177 (Lu-177), and iodine-131 (I-131) were then determined to assess the accuracy of quantitative imaging for internal renal dosimetry.
Tran-Gia noted, ‟Although in our study the kidneys were modeled as a relatively simple one-compartment model, the study represents an important step towards a reliable determination of absorbed doses and, therefore, an individualized patient dosimetry of other critical organs in addition to kidneys.”
Ultimately, affordable 3-D printing techniques hold the potential for manufacturing individualized anthropomorphic phantoms in many nuclear medicine clinical applications.
For more information: www.jnm.snmjournals.org


 July 30, 2024
July 30, 2024