December 8, 2014 — Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia. As many as 5 million Americans are affected, a number expected to grow to 14 million by 2050, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Preventive treatments may be most effective before Alzheimer's disease is diagnosed, such as when a person is suffering from mild cognitive impairment (MCI), a decline in cognitive skills that is noticeable but not severe enough to affect independent function. Previous efforts at early detection have focused on beta amyloid, a protein found in abnormally high amounts in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease.
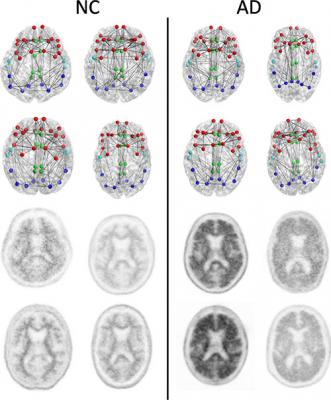
For this study, researchers looked at the brain's structural connectome, a map of white matter tracts that carry signals between different areas of the brain, which provides a way to characterize and measure these connections and how they change through disease or age.
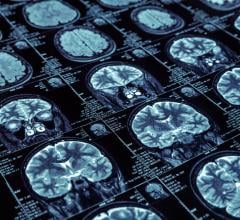
Results from 102 patients enrolled in a national study called the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) 2 were analyzed. The patients had undergone diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), an MRI method that assesses the integrity of white matter tracts in the brain by measuring how easy it is for water to move along them.
The researchers correlated changes in the structural connectome with results from florbetapir positron emission tomography (PET) imaging, a technique that measures the amount of beta amyloid plaque in the brain. Increased florbetapir uptake corresponds with greater amounts of the protein.
The results showed a strong association between florbetapir uptake and decreases in strength of the structural connectome in each of the five areas of the brain studied.
"This study ties together two of the major changes in the Alzheimer's brain—structural tissue changes and pathological amyloid plaque deposition—and suggests a promising role for DTI as a possible diagnostic adjunct," said Jeffrey W. Prescott, M.D., Ph.D.
Based on these findings, DTI may offer a role in assessing brain damage in early Alzheimer's disease and monitoring the effect of new therapies.
"Traditionally, Alzheimer's disease is believed to exert its effects on thinking via damage to the brain's gray matter, where most of the nerve cells are concentrated," said Jeffrey R. Petrella, M.D., professor of radiology at Duke and senior author on the study. "This study suggests that amyloid deposition in the gray matter affects the associated white matter connections, which are essential for conducting messages across the billions of nerve cells in the brain, allowing for all aspects of mental function."
"We suspect that as amyloid plaque load in the gray matter increases, the brain's white matter starts to break down or malfunction and lose its ability to move water and neurochemicals efficiently," added Prescott.
The researchers plan to continue studying this cohort of patients over time to gain a better understanding of how the disease evolves in individual patients. They also intend to incorporate functional imaging into their research to learn about how the relationship between function and structure is affected with increasing amyloid burden.
This study was presented at RSNA 2014.
Other co-authors on the study are P. Murali Doraiswamy, M.D. and Kingshuk R. Choudhury, Ph.D.
For more information: www.rsna.org


 July 25, 2024
July 25, 2024