September 25, 2014 — Cellular therapeutics, which uses intact cells to treat and cure disease, is a promising new approach in medicine but is hindered by the inability of doctors and scientists to effectively track the movements, destination and persistence of these cells in patients without resorting to invasive procedures, like tissue sampling.
In a paper published Sept. 17 in the online journal Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, researchers at University of California, San Diego (UCSD) School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh and elsewhere describe the first human tests of using a perfluorocarbon (PFC) tracer in combination with noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to track therapeutic immune cells injected into patients with colorectal cancer.
“Initially, we see this technique used for clinical trials that involve tests of new cell therapies,” said first author Eric T. Ahrens, Ph.D., professor in the department of radiology at UCSD. “Clinical development of cell therapies can be accelerated by providing feedback regarding cell motility, optimal delivery routes, individual therapeutic doses and engraftment success.”
Currently, there is no accepted way to image cells in the human body that covers a broad range of cell types and diseases. Earlier techniques have used metal ion-based vascular MRI contrast agents and radioisotopes. The former have proven difficult to differentiate in vivo; the latter raise concerns about radiation toxicity and do not provide the anatomical detail available with MRI.
“This is the first human PFC cell tracking agent, which is a new way to do MRI cell tracking,” said Ahrens. “It’s the first example of a clinical MRI agent designed specifically for cell tracking.”
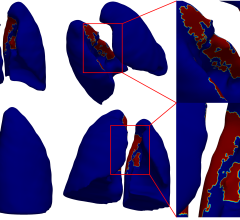
Researchers used a PFC tracer agent and an MRI technique that directly detects fluorine atoms in labeled cells. Fluorine atoms naturally occur in extremely low concentrations in the body, making it easier to observe cells labeled with fluorine using MRI. In this case, the modified and labeled dendritic cells – potent stimulators of the immune system – were first prepared from white blood cells extracted from the patient. The cells were then injected into patients with stage 4 metastatic colorectal cancer to stimulate an anti-cancer T-cell immune response.
The published study did not assess the efficacy of the cell therapy, but rather the ability of researchers to detect the labeled cells and monitor what happened to them. Ahrens said the technique worked as expected, with the surprising finding that only half of the delivered cell vaccine remained at the inoculation site after 24 hours.
“The imaging agent technology has been to shown to be able to tag any cell type that is of interest,” Ahrens said. “It is a platform imaging technology for a wide range of diseases and applications,” which might also speed development of relevant therapies.
“Noninvasive cell tracking may help lower regulatory barriers,” Ahrens explained. “For example, new stem cell therapies can be slow to obtain regulatory approvals in part because it is difficult, if not impossible, with current approaches to verify survival and location of transplanted cells. And cell therapy trials generally have a high cost per patient. Tools that allow the investigator to gain a ‘richer’ data set from individual patients mean it may be possible to reduce patient numbers enrolled in a trial, thus reducing total trial cost.”
Co-authors include Brooke M. Helfer and Charles F. O’Hanlon, Celsense Inc.; and Claudiu Schirda, University of Pittsburgh.
Funding support came, in part, from the National Institutes of Health (grant R01-CA13463) and the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
For more information: www.health.ucsd.edu


 July 25, 2024
July 25, 2024