A balance board accessory for a popular video game console can help people with multiple sclerosis (MS) reduce their risk of accidental falls, according to new research published online in the journal Radiology. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans showed that use of the Nintendo Wii Balance Board system appears to induce favorable changes in brain connections associated with balance and movement.
Balance impairment is one of the most common and disabling symptoms of MS, a disease of the central nervous system in which the body’s immune system attacks the protective sheath around nerve fibers. Physical rehabilitation is often used to preserve balance, and one of the more promising new tools is the Wii Balance Board System, a battery-powered device about the size and shape of a bathroom scale. Users stand on the board and shift their weight as they follow the action on the television screen during games like slalom skiing.
While Wii balance board rehabilitation has been reported as effective in patients with MS, little is known about the underlying physiological basis for any improvements in balance.
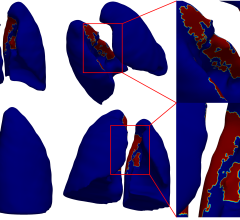
Researchers recently used an MRI technique called diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to study changes in the brains of 27 MS patients who underwent a 12-week intervention using Wii balance board-based visual feedback training. DTI is a non-conventional MRI technique that allows detailed analysis of the white matter tracts that transmit nervous signals through the brain and body.
MRI scans of the MS patients showed significant effects in nerve tracts that are important in balance and movement. The changes seen on MRI correlated with improvements in balance as measured by an assessment technique called posturography.
These brain changes in MS patients are likely a manifestation of neural plasticity, or the ability of the brain to adapt and form new connections throughout life, according to lead author Luca Prosperini, M.D., Ph.D., from Sapienza University in Rome, Italy.
“The most important finding in this study is that a task-oriented and repetitive training aimed at managing a specific symptom is highly effective and induces brain plasticity,” he said. “More specifically, the improvements promoted by the Wii balance board can reduce the risk of accidental falls in patients with MS, thereby reducing the risk of fall-related comorbidities like trauma and fractures.”
Prosperini noted that similar plasticity has been described in persons who play video games, but the exact mechanisms behind the phenomenon are still unknown. He hypothesized that changes can occur at the cellular level within the brain and may be related to myelination, the process of building the protective sheath around the nerves.
The rehabilitation-induced improvements did not persist after the patients discontinued the training protocol, Prosperini said, most likely because certain skills related to structural changes to the brain after an injury need to be maintained through training.
“This finding should have an important impact on the rehabilitation process of patients, suggesting that they need ongoing exercises to maintain good performance in daily living activities,” Prosperini concluded.


 July 25, 2024
July 25, 2024