April 11, 2014 — A University of Colorado Cancer Center study presented at the 2014 annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) describes a novel method to "manipulate the lipid metabolism in the cancer cell to trick them to use more radiolabeled glucose, the basis of PET [positron emission tomography] scanning," according to Isabel Schlaepfer, Ph.D., investigator at the CU Cancer Center Department of Pharmacology and recipient of a 2014 Minority Scholar Award in Cancer Research from AACR.
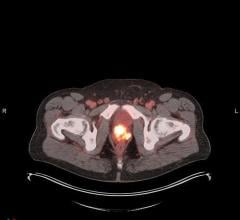
The body's cells have two major interconnected energy sources: the lipid metabolism and the glucose metabolism. Most cancers feed themselves by metabolizing glucose, and thus can be seen in PET scans that detect radiolabeled glucose. However, prostate cancers tend to use the lipid metabolism route and so cannot be imaged in this way effectively.
The current study used the clinically safe drug etomoxir to block prostate cancer cells' ability to oxidize lipids. With the lipid energy source removed, cells switched to glucose metabolism and both cells and mouse models roughly doubled their uptake of radiolabeled glucose.
"Because prostate cancer can be a slow-growing disease, instead of immediate treatment, many men choose active surveillance — they watch and wait. But that requires repeated prostate biopsies. Instead, now we could use this metabolic technique to allow PET imaging to monitor prostate cancer progression without the need for so many biopsies," said Schlaepfer.
Schlaepfer also points out possible therapeutic application of the technique; while immediately useful for imaging, it may be that cutting off a prostate cancer cell's ability to supply itself with energy from lipids could make it difficult for these cells to survive.
For more information: www.ucdenver.edu

 July 30, 2024
July 30, 2024