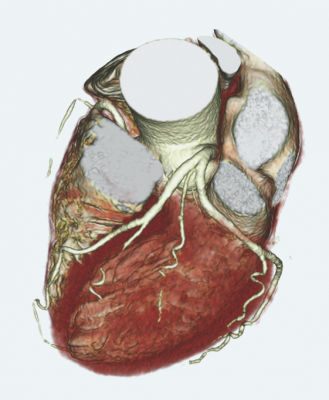
August 30, 2012 — An ultra-fast, 320-detector computed tomography (CT) scanner can accurately sort out which people with chest pain need – or don’t need – an invasive procedure such as cardiac angioplasty or bypass surgery to restore blood flow to the heart, according to an international study. Results of the study, which involved 381 patients at 16 hospitals in eight countries, were presented at the European Society of Cardiology Congress in Munich, Germany, on Aug. 28.
“The CORE 320 study is the first prospective, multicenter study to examine the diagnostic accuracy of CT for assessing blockages in blood vessels and determining which of those blockages may be preventing the heart from getting adequate blood flow,” said Joao A. C. Lima, M.D., senior author of the study and professor of medicine and radiology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. “We found an excellent correlation in results when we compared the 320-detector CT testing with the traditional means of assessment using a stress test with imaging and cardiac catheterization.”
The study findings, said Lima, would apply to people who have chest pain but are not having a heart attack. Many people in that situation are sent to a cardiac catheterization laboratory for further evaluation with angiography, an invasive test to look for blockages in the coronary arteries using dye and special X-rays. About 30 percent of people who have such catheterization are found to have minimal disease or no blockage requiring an intervention to open or bypass the vessel.
Lima explained that a nuclear medicine stress test with imaging, known as SPECT (single-photon emission computed tomography), shows reduced blood flow to the heart without indicating the number or specific location of blockages.
The 381 patients who completed the study had traditional SPECT tests and invasive angiography. They also had two types of tests with a noninvasive 320-detector CT scanner. In the first CT test, the scanner was used to see the anatomy of vessels to assess whether and where there were blockages (angiography). Then, in a second CT test with the same machine, patients were given a vasodilator, a medicine that dilates blood vessels and increases blood flow to the heart in ways similar to what happens during a stress test (CT perfusion [CTP])
According to lead author Carlos E. Rochitte, M.D., a cardiologist at the Instituto do Coracao in Sao Paulo, Brazil, “We found that the 320-detector CT scanner allowed us to see the anatomy of the blockages as well as determine whether the blockages were causing a lack of perfusion to the heart. We were therefore able to correctly identify the patients who needed revascularization within 30 days of their evaluation.”
“Many patients are sent for an angioplasty when they may not need it. Our ultimate goal is to have more certainty about which patients having chest pain – without evidence of a heart attack – need an invasive procedure to open an arterial blockage,” said cardiologist Richard George, M.D., assistant professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and a co-author of the study. “The CTP test added significant information about the patients’ conditions and boosted our ability to identify those whose blockages were severe enough to reduce blood flow to the heart.”
The 320-slice detector provides a complete picture of the heart by making just one revolution around the body. The researchers say the two tests combined – CTA and CTP – still produce less radiation than a scan with the 64-detector in widespread use today. “In our study, the amount of radiation exposure to patients from the two 320-detector CT scanner tests was half the amount they received as a result of the traditional evaluation methods – the angiogram and nuclear medicine stress test combined,” says Lima.
The researchers will continue to follow the patients in the study for up to five years, looking for any heart-related events such as heart attacks, as well as hospital admissions, procedures or surgeries.
Hospitals that participated in the CORE 320 study are located in the United States, Germany, Canada, Brazil, the Netherlands, Denmark, Japan and Singapore. Images obtained during the study were evaluated in core laboratories at Johns Hopkins and at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. The study was sponsored by Toshiba Medical Systems.
Johns Hopkins researchers collaborated with Toshiba on the development of the 320-detector CT scanner used in the study. In 2007, Johns Hopkins was one of three sites that participated in worldwide beta testing of the scanner that served as the prototype of the 320-detector system. Feedback provided by Johns Hopkins researchers was instrumental in the development of the scanner, which is now the only 320-detector CT scanner on the market.
For more information: www.hopkinsmedicine.org


 August 09, 2024
August 09, 2024