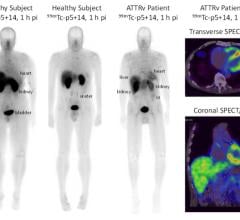
March 1, 2012 — Cell>Point announced it entered into a licensing agreement for South Korea, Taiwan, Malaysia, Vietnam and the Philippines with Hyun Imc Co. Ltd., headquartered in Seoul, South Korea, for the kit manufacture, marketing and distribution of Cell>Point’s cancer and cardiology nuclear imaging product.
The product is based on its technetium-99m-labeled ethylenedicysteine-n-acetyl-glucosamine (99mTc-EC-G) radiotracer. Hyun Imc will be responsible for sponsoring clinical studies and seeking regulatory approval in each of the countries covered by the license. Cell>Point will receive an upfront payment, and development and regulatory milestone payments, as well as royalties on gross sales from Hyun Imc.
99mTc-EC-G, invented at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and acquired by Cell>Point, is a target-specific molecular imaging radiopharmaceutical that has moved into a Phase 3 lung cancer imaging trial and Phase 2 cardiology imaging trial. It is injected intravenously and then imaged using a single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) camera.
99mTc-EC-G Phase 3 lung cancer imaging trial
For the Phase 3 lung cancer study, all patients will be imaged on combination SPECT/CT (computerized tomography) and PET/CT cameras. Where combination cameras are not available, a special workstation will be used to integrate the patient images taken from the stand-alone SPECT or PET cameras, as the case may be. Using a workstation to integrate the images allows the medical site to take full advantage of 99mTc-EC-G without the need for a new combination SPECT/CT camera on the premises. This should significantly expand the utilization of the installed SPECT camera base in the United States and the rest of the world, which is already orders-of-magnitude greater than the PET camera base. The lung cancer trial will be followed by Phase 4 trials in lymphoma and breast, liver, colorectal, prostate, and head and neck cancers.
99mTc-EC-G Phase 2 cardiology imaging trial
In a separate clinical trial, 99mTc-EC-G has moved from a Phase 1b to a Phase 2 cardiovascular imaging study. The product is the same as that used in the oncology trials. 99mTc-EC-G exhibits very low uptake in the normal heart; however, it exhibits very high uptake in heart areas that have suffered ischemia (i.e., profound deprivation of blood flow), such as a myocardial infarction. The Phase 2 cardiovascular trial will involve patients who have suspected coronary artery disease and compare 99mTc-EC-G images of the heart with images obtained from a full “stress/rest” myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) study.
It should be noted that one of the objectives of the study is to compare the results from the “rest” only portion of the 99mTc-EC-G study to the results from the full “stress/rest” MPI study. Based on clinical evidence from the previous Phase 1b study, Cell>Point believes clinical information learned from the 99mTc-EC-G “rest” study will be potentially greater than that of the full “stress/rest” MPI study, which uses 99mTc-sestamibi for the stress image and thallium-201 for the rest image and takes five to seven hours. If the “rest” only 99mTc-EC-G study yields as good as or greater clinical information compared to traditional MPI, then the 99mTc-EC-G rest study—which can be conducted in 30 to 45 minutes — should dramatically improve cardiovascular imaging.
For more information: www.cellpointweb.com

 July 30, 2024
July 30, 2024