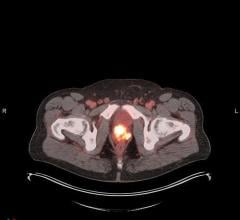
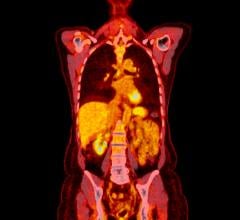
April 8, 2011 – At the American College of Cardiology (ACC) Annual Scientific Meeting in New Orleans, Siemens Healthcare demonstrated how users of nuclear imaging systems can use its IQ•SPECT to help reduce the length of imaging protocols.
A field-upgradeable combination of hardware and software, IQ•SPECT is available on the company’s Symbia S and Symbia T series single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and SPECT-CT systems. The company says it is helping nuclear cardiologists cut the cardiac imaging protocol from 20 minutes to less than five minutes. These shortened exams can potentially reduce radiation dose and provide high quality diagnostic information.
“There is a significant difference between a four-minute SPECT scan with IQ•SPECT and a conventional 20-minute SPECT because many older patients cannot tolerate a longer scan,” said James R. Corbett, M.D., director, cardiovascular nuclear medicine, professor, departments of internal medicine and radiology, University Hospital, University of Michigan Health System. “In our practice IQ•SPECT provides the opportunity to obtain quality SPECT imaging information in cases where it would not have been possible to even attempt imaging.”
Siemens recently received the Product Differentiation Excellence Award, Nuclear Cardiology, North America, 2011, from Frost and Sullivan.
“Despite the benefits to clinical decision making conferred by the modality, the cardiac SPECT market has been faced with challenging circumstances that have led to a significant shift in the traditional provider setting,” said Sangeetha Prabakar, industry analyst, Frost and Sullivan. “With IQ•SPECT, Siemens has delivered a solution that addresses the cost sensibilities engendered by decreased reimbursement and the relative scarcity of the radiotracer. Using a field-upgradeable approach to providing high-quality imaging in almost a quarter of the time of conventional SPECT, Siemens has clearly demonstrated its leadership in this space.”
Siemens said the technology has been shown to reduce radiotracer doses by up to 50 percent, translating into lower amounts of radiation for the patient and potential cost savings. IQ•SPECT utilizes Smartzoom collimators, which focus on the heart, collecting up to four times more counts than conventional, large-bore, parallel-hole collimators. It also uses cardio-centric orbit acquisition, which ensures that the heart is always in the collimator’s magnification zone, as opposed to the gantry’s mechanical center. A 3-D reconstruction algorithm models the position of each of the 48,000 collimator holes on each detector, allowing distant-dependent isotropic (3-D) resolution recovery, CT-based attenuation correction and energy window-based scatter correction.
For more information: www.siemens.com/healthcare


 November 12, 2025
November 12, 2025