August 6, 2010 - The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has given clearance to a computer-aided detection product used in the interpretation of virtual colonoscopy exams.
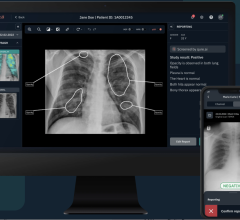
VeraLook from iCAD uses sophisticated interpretive technology to automatically identify polyps in images produced from a virtual colonoscopy, also known as CT colonography (CTC).
“This breakthrough technology will aid radiologists in detecting and highlighting suspicious areas that could be missed during an initial review of a virtual colonoscopy exam,” said Abraham Dachman, M.D., professor of radiology and director of fellowship programs at the University of Chicago. “As with breast and prostate cancer detection, computer-aided detection for virtual colonoscopy will help us find more cancers at an earlier stage.”
The identified polyps can then be highlighted to the interpreting physician after initial review of the CTC exam with the intent of identifying additional potential polyps that may not have been identified on initial review.
Extensive testing by radiologists has demonstrated that the use of VeraLook improved reader sensitivity to all colonic polyps 6 mm or larger in size in a statistically significant manner and particularly for smaller, more easily missed polyps and precancerous polyps which can develop into malignancies over time.
VeraLook has also demonstrated high standalone sensitivity to detecting polyps, while generating a low number of clinically acceptable false positive marks on CTC images. Reader and standalone testing was conducted using exams containing various types of polyps and on patients prepped using different methodologies.
According to the American Cancer Society, colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States.
Because it requires no sedation, patients undergoing a CTC exam are able to return to their normal activities immediately following the examination.
For more information: www.icadmed.com


 August 09, 2024
August 09, 2024