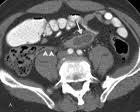
June 1, 2010 - When computed tomography (CT) results suggest appendicitis, but a patient’s symptoms are inconsistent with the acute condition, physicians should consider a diagnosis of chronic or recurrent appendicitis and surgical treatment, according to a new study published in the online edition and July printed issue of the journal Radiology.
“The decision to forego surgery in these patients often results in missed appendicitis, with a possible increased risk of perforation,” said study co-author Emily M. Webb, M.D., assistant professor of clinical radiology at the University of California, San Francisco.
Acute appendicitis, which occurs when the appendix — a small, tube-like structure attached to the large intestine — becomes blocked and inflamed, requires prompt surgical removal. Left untreated, an inflamed appendix will eventually perforate, or burst, spilling infectious materials into the abdominal cavity, which can be life-threatening. In the less common chronic and recurrent appendicitis, patients experience milder symptoms that may come and go. According to the National Institutes of Health, appendicitis can affect anyone, but is more common among people 10 to 30 years old. Appendicitis leads to more emergency abdominal surgeries than any other cause.
For the study, the researchers reviewed CT reports and medical records of 2,283 patients who underwent CT for suspected appendicitis at the University of California, San Francisco Medical Center between 2002 and 2007. Patients in the study included 856 men and 1,427 women between the ages of 18 and 99 years old with a mean age of 46.
“We wanted to look at patients with a positive CT scan but atypical clinical symptoms who did not have their appendix immediately removed,” Dr. Webb said.
Of the study’s 2,283 patients, 516, or 23 percent, had CT findings that indicated a probable or definite appendicitis. Of those 516 patients, 450 (87 percent) had their appendix surgically removed within four days. Ninety-five percent of those cases were confirmed as acute appendicitis.
Forty-nine (10%) of 516 patients had nonsurgical treatment, including antibiotics or percutaneous abscess drainage. An additional four of 516 patients were lost to follow up.
Thirteen (three percent) of the 516 patients with positive CT findings did not receive immediate surgical treatment because their symptoms — including a normal appetite, absence of nausea and vomiting, normal white blood cell count and mild or resolving pain — were atypical for acute appendicitis. Of those, five (38 percent) ultimately had their appendix removed after seeking treatment for the same symptoms an average of four months later. Appendicitis was confirmed in all cases.
“The results of our study confirm that CT is a good diagnostic tool for appendicitis and that surgeons should be wary of dismissing positive CT findings,” Dr. Webb said. “Prompt treatment of chronic or recurrent appendicitis can prevent patients from developing complications or other future ill effects.”
The study’s findings may also help explain the disparity between CT results that indicate appendicitis and patient symptoms that do not.
“When the appendix is not completely obstructed, it can result in a milder form of appendicitis that is chronic or recurring,” Dr. Webb said. “But the three forms of appendicitis, acute, chronic and recurrent, are indistinguishable on CT scans.
For more information: www.rsna.org


 August 09, 2024
August 09, 2024