January 25, 2010 - One out of 50 people in the United States has an unruptured brain aneurysm, and about 40 percent of all people who have a ruptured brain aneurysm will die as a result.
That is why radiologists at Mayo Clinic are using an aneurysm detection system to detect aneurysms with far greater speed and accuracy. Since adopting the method, they have achieved a 95 percent accuracy rate in detecting aneurysms compared with 70 percent for manual interpretation.
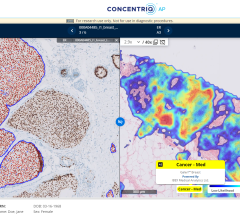
The project has examined more than 15 million images from thousands of patients since the project began in early July. It uses technology that combines advanced imaging with analytics to highlight likely aneurysms for faster detection. This helps radiologists identify them before they result in brain hemorrhage or neurological damage.
To improve the process of detection using noninvasive magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) imaging technology, Mayo Clinic and IBM worked to create automatic reads that run detection algorithms immediately following a scan.
Once images are acquired, they are automatically routed to servers in the Mayo and IBM Medical Imaging Informatics Innovation Center located on the Mayo campus in Rochester, a collaborative research facility that combines advanced computing and image processing to provide faster, more accurate image analysis. There algorithms align and analyze images to locate and mark potential aneurysms — even very small ones less than 5mm — so specially trained radiologists can conduct a further and final analysis.
From the time an image is taken to the time it is ready to be read by a radiologist, there often is only a 10-minute window. The systems identifies images generated off the scanner and routes those related to the head and brain through the special workflow, which then conducts automated aneurysm detection. On average, this can be done in three to five minutes, improving efficiency and saving valuable radiologist's time, leading to a quicker diagnosis which is especially important in the case of a serious aneurysm.
The aneurysm detection system uses an algorithm developed by Mayo researchers that is executed on IBM WebSphere Process Server to model and orchestrate the automated workflow. Images are stored on IBM DB2 for Linux and Windows data service and workflow logic is run on IBM System x servers and IBM storage.
In the future, Mayo Clinic expects to use the same approach for other radiology detection tests such as the diagnosis of cancer or vessel anomalies in other parts of the body.
The findings in the study were reported in the November 24, 2009, online issue Journal of Digital Imaging.
For more information: www.ibm.com/think

 July 26, 2024
July 26, 2024