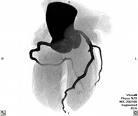
January 6, 2010 - The image quality of multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) scans used for the noninvasive detection of coronary artery disease can be significantly affected by patient characteristics, such as ethnicity, body mass index (BMI), and heart rate. Researchers explained the details of these findings from a large multicenter international trial in the January issue of the American Journal of Roentgenology.
The large multicenter international trial study included 291 patients with coronary artery calcification and found that compared with examinations of white patients, studies of black patients had significantly poorer image quality.
In the study, led by Melvin E. Clouse, M.D., researchers found that diagnostic accuracy of MDCT are limited by physiologic factors when compared conventional invasive coronary angiography. These factors included high heart rate, arrhythmia, obesity, and high coronary calcium burden with motion. The study was significant because it showed a relevant influence of BMI, heart rate, ethnicity, and breathing artifact on the degradation of image quality.
Dr. Clouse added that the diagnostic ability of any imaging method is directly dependent on image quality.
For more information: www.jacr.org


 August 09, 2024
August 09, 2024